The first aerobatic glider designed by Hans Jacob.
Glider
IST/PAF ARDA XL-10B Balang / Grasshopper
The XL-10B Balang (Grasshopper) was a powered glider joint project of Institute of Science and Technology (IST) and Philippine Air Force (PAF) Air Research and Development Authority (ARDA).
It first flew in 1953.
Engine: 20 hp
Wingspan: 12 m
Length: 5.20 m
Height: 1.5 m
Aspect ratio: 8.1
Wing area: 17.8 sq,m
Empty weight: 185 kg
Loaded weight: 280 kg
Max speed: 125 kph
Cruise speed: 72-80 kph
Stall: 49 kph
Glide speed: 75 mph
Issoire PIK-30 / Societe Siren PIK-30 / Eiri Avion PIK 30

Issoire, part of the groupe Siren, acquired a license from Eiri Avion to build the 15 m. self- launching Finnish PIK 20E designed by Pekka Tammi and M.Moniot. The Pik 30 is a self- launching 17 m. development which first flew in 1984. It has the capability of being flown as a 15 m. sailplane or, with tip extensions, with 17 m. span. The PIK 30 has a mast mounted manually actuated retractable engine.
Construction of the wings and tail surfaces: GFRP sandwich with PVC core; carbon fiber spar caps and cockpit sides: GFRP monocoque structure reinforced with ribs of carbon fiber.

Span: 17m / 55.8ft
Area: 10.63sq.m / 114.42sq.ft
Empty Weight: 340kg / 750lb
Payload: 120kg / 264lb
Gross Weight: 460kg / 1014lb
Wing Load: 43.27 kg
/sq.m / 8.86 lb/sq.ft
Water Ballast: 0
Aspect ratio: 27.2
L/DMax: 45 110 kph / 59 kt / 68 mph
MinSink: 0.54 m/s / 1.77 fps / 1.05 kt
Airfoil: Wortmann FX-67 K170, root, K150, tip
Engine: 32 kW/ 43 bhp Rotax 503
Seats: 1
No. Built: 10
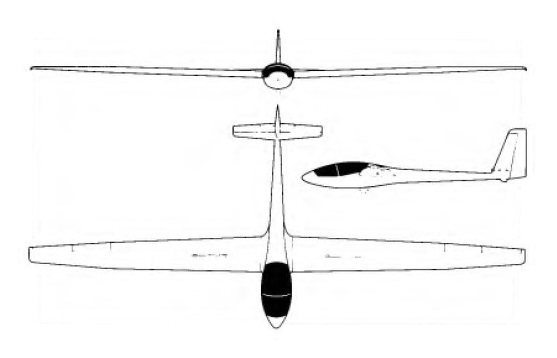
Issoire E 78 Silene

The E 78 Silene side-by-side two-seat sailplane was developed by CERVA (Consortium Europeen de Realisation et de Ventes d’Avions) and is the first French glassfibre two-seater. The company was owned by Siren SA and Wassmer-Aviation SA. The E 78 was designed by Siren and, following the closure of Wassmer, was transferred to Issoire in late 1977. The aim was to produce a sailplane suitable for all stages of glider training from ab initio to cross-country flights.
Construction was started in February 1973 and the prototype first flew at Argenton on 2 July 1974.
The wings are of glassfibre/plastic foam sandwich construction, incorporating two-section ailerons of similar material and Schempp-Hirth airbrakes operating both above and below each wing. Flaps are not fitted. The fuselage is a semi-monocoque glassfibre/plastic foam sandwich structure. The conventional tail unit incorporates a fixed incidence tailplane and trim tabs on each elevator.
The pilots sit in staggered position to keep the width of the fuselage to a minimum, the starboard seat being set slightly to the rear. The Silene is available with either retractable or fixed landing wheel with hydraulic brake and shock absorber.
E 78 Silene
Wing span: 18.0 m / 59 ft 0 3/4 in
Length: 7.95 m / 26 ft 1 in
Height: 1.5 m / 4 ft 11 in
Wing area: 18.0 sq.m / 193.8 sq ft
Wing section: Berlin E55 166
Aspect ratio: 18.0
Empty weight: 365 kg / 805 lb
Max weight: 565 kg / 1,246 lb
Water ballast: None
Max wing loading: 29 kg/sq.m / 5.94 lb/sq ft
Max speed: 119 kt / 220 km/h
Stalling speed: 34 kt / 63 km/h
Min sinking speed: 0.59 m/sec / 1.8 ft/sec at 39 kt / 73 km/h
Best glide ratio: 38 at 51 kt / 95 km/h
Issoire Aviation
Societe Issoire Aviation was formed in 1978, following the bankruptcy of Wassmer Aviation, by President/General Director of Siren SA. In addition to subcontract work for the French aircraft industry and construction of sailplanes, offered IA 80 Piranha as a two-seat lightplane.
1995 saw the takeover of Issoire Aviation by the REXIAA Group. Alongside the subcontracting activities, launch of the LIONCEAU programme, the first “all carbon” aircraft with the participation of all the companies in the group.
ISF Mistral / Mistral Flugzeugbau Mistral

Developed from the original Mistral, which first flew in 1975, the ISF Model 2 Mistral-C single-seat Club Class sailplane is a product of the German firm Ingenieur/Buro Dipling Strauber – Frommhold GmbH & Co KG. Design work on the Mistral-C, which was intended to conform with the new FAI Club regulations, started in October 1974 and the prototype made its first flight in October 1976; 20 examples of this glassfibre T-tailed sailplane had been completed by the beginning of 1979. The type took 3rd place out of 33 contestants in the first Club class international competition held in Sweden in 1979.
The Mistral-C is a cantilever shoulder wing monoplane with 1° forward sweep at the quarterchord line; the wings and tail unit are of glassfibre reinforced plastic/foam/Conticell CC60 sandwich construction, the ailerons being of glassfibre reinforced plastic (GRP). There are Schempp-Hirth aluminium air brakes in the wing upper surfaces.

The fuselage is a GRP monocoque structure, and the landing gear consists of a non-retractable monowheel with a brake, and a tailskid. The tailplane is a fixed incidence one with spring trim, and the pilot sits under a large flush-fitting one-piece canopy that opens sideways. There is a towing hook on the centre of gravity, and a nose-mounted hook is optional.
In 1980 Mistral Flugzeugbau was formed to continue production of the Mistral-C at Hassfurt/Main; it had previously been built at Bensheim.
Mistral-C
Span: 15.0 m / 49 ft 2.5 in
Length: 6.73 m / 22 ft 1 in
Height: 1.45 m / 4 ft 9 in
Wing area: 10.9 sq.m / 116.8 sqft
Aspect ratio: 20.7
Wing section: Wortmann FX-61-163
Empty weight: 230 kg / 510 lb
Max weight: 350 kg / 77 1 lb
Water ballast: None
Max speed: 155 mph 135 kt / 250 km/h (in smooth air)
Max aero-tow speed: 105 mph
Stalling speed: 33 kt / 62 km/h
Min sinking speed: 2.17 ft/sec at 43.5 mph
Min sinking speed: 0.60 m/sec / 1.96 ft/sec at 35 kt / 65 km/h
Best glide ratio: 35: 1 at 55.5 mph
Best glide ratio: 35 at 49 kt / 90 km/h

Isaac, A.C.T.
Mr A.C.T. Isaac, of London, later of Hillmorton, near Rugby, Warwickshire, in the UK, built a two-seat primary gliders. The first, in 1923 had trials off Parliament Hill,in North London, resulted in the gliders either breaking up and injuring the pilot, or in requests from the police to ‘take them away’.
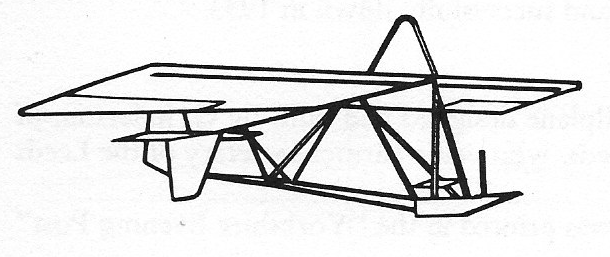
A two seat primary type with 9.29 sq.m / 100 sq.ft wing area with a slotted section.
It was left overnight in dead-calm conditions. The following morning it was not to be seen, and was presumed stolen.
A second machine was built in 1929 to Zogling-like specification but this too was a failure. The flexible structure was abandoned as impracticable. The empty was 45.35 kg / 100 lb.
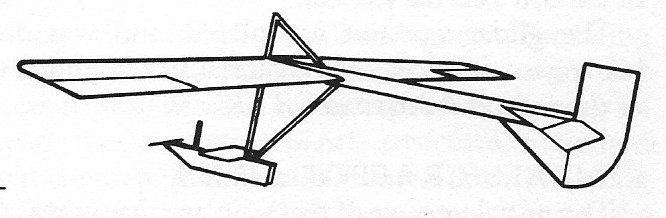
A biplane glider of 7.32m / 24 ft 0 in span was later built and test flown at Chingford, London.
IPE KW 1 / KW 1 Quero Quero

This Brazilian single-seater training glider, known in full as the IPE KW 1 b 2 Quero Quero II, is a development of the original KW 1 designed by Ing Kuno Wiedmaier and made its first flight on 1 October 1972.
The Quero Quero is a cantilever high wing monoplane with the same Wortmann wing section as the Scheibe SF-30 Club-Spatz, which it somewhat resembles, and is of wood and Brazilian pine plywood construction. There are spoilers in the wing upper and lower surfaces, and the wing tips are turned down to provide an endplate effect. Landing gear consists of a non-retractable monowheel and a tailwheel, and the pilot sits under a one-piece detachable cockpit canopy.
Certification from the Brazilian CTA in the semi-aerobatic category, with an extension for cloud flying, was awarded in December 1976 and the Quero Quero II was put into production by IPE – Industria Paranaense de Estruturas at Curitiba in the state of Parana. By 31 March 1979 IPE had completed 28 Quero Queros, consisting of one static test and three flying prototypes, a pre-series of four production aircraft, one of which was lost in a nonfatal accident, and all of a second-series batch of 20 Mk IIs, which were in service with various Brazilian clubs.
Quero Quero II
Span:49ft 2.5 in
Length: 21 ft 2.75 in
Height: 4 ft 4.75 in
Wing area :125.9 sq ft
Aspect ratio: 18.0
Empty weight: 374 lb
Max weight. 595 lb
Max speed: 93 mph (in smooth air)
Min sinking speed: 2.10 ft/sec at 38.5 mph
Best glide ratio: 28:1 at 45 mph
IPE 02 Nhapecam
The 02 tandem two-seater, known as the Nhapecam, is the second training sailplane from the Brazilian firm of IPE – Industrie Paranaense de Estruturas at Curitiba, and has been under development for some months; it made its first flight on 24 May 1979.
The 02 is a cantilever shoulder wing monoplane with a modified Scheibe SF-30 Club-Spatz wing section; it is rather larger than the Quero Quero II, with a span of 16.60m (54ft 5Vain), a longer, more pointed nose and a lengthened one-piece cockpit canopy under which the two pilots sit. There are spoilers in the wing upper and lower surfaces, and the landing gear consists of a non-retractable monowheel and a tailwheel. A powered version of the 02, the IPE 03, was under development; this has a repositioned low wing and a retractable landing gear, and probably a 60hp Limbach powerplant.
An order for at least 30 IPE 02s for the Brazilian Clubs was confirmed in 1980.
Span: 54 ft 5.5 in
Length: 25 ft 11 in
Height: 4 ft 11 in
Wing area: 170.1 sqft
Aspect ratio: 16.6
Empty weight: 551 lb
Max weight: 1,058 lb
Max speed: 124 mph (in smooth air)
Min sinking speed: 2.13 ft/sec
Best glide ratio: 30:1 at 50 mph
I.O.W. Gliding Club
A primary type glider, with an all-metal fuselage, was under construction by the I.O.W. Gliding Club in 1931. The only reference found appeared in “Sailplane and Glide” Volume 2, No.3.