Junkers and Messerschmitt competed in 1940 to design and develop a very large transport glider suitable for the delivery of men or materials. Junkers’ Ju 322 Mammut (Mammoth) spanned 62.0m and would have accommodated more than 100 fully equipped troops, but when tested proved to be unstable and was cancelled by the Reichsluftfahrtministeriurn.
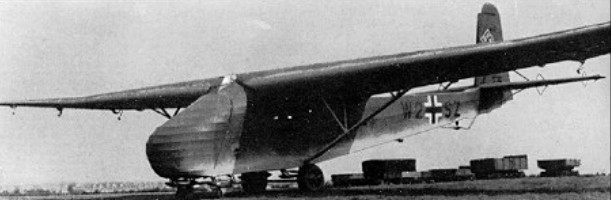
Messerschmitt’s Me 321 was a most successful design of braced high-wing configuration and with construction of welded steel tube, wood and fabric. The pilot was high on the fuselage in a single-seat cockpit, adjacent to the wing’s leading edge. Access to the main cabin was via large clamshell doors in the nose or by doors on each side of the rear fuselage.
The Me 321 VI prototype flew first in March 1941 and Me 321A-1 production aircraft entered service in May of that year. The later Me 321B-1 had a crew of three and defensive armament of four 7.9mm MG 15 machine-guns. Me 321 (175 built) were towed usually by a trio of Bf 110C or by the five-engined Heinkel He 111Z. Rocket units could be used to assist take-off from rough fields.
The Messerschmitt Me 321 spanned 54.68 m (180 ft), and was intended to ferry into combat 22.5 tonnes (22 tons) of equipment or a company of soldiers complete with 88 mm flak gun or tracked vehicle.