San Diego CA.
USA
Circa 1917 built a biplane
San Diego CA.
USA
Circa 1917 built a biplane

A 1916 five-seat biplane flying-boat powered by a single Fiat A.12bis or Lorraine engine. Several were operated commercially.
S.16ter
Max take-off weight: 2652 kg / 5847 lb
Empty weight: 1852 kg / 4083 lb
Wingspan: 15.5 m / 51 ft 10 in
Length: 9.89 m / 32 ft 5 in
Height: 3.67 m / 12 ft 0 in
Wing area: 52 sq.m / 559.72 sq ft
Max. speed: 194 km/h / 121 mph
Ceiling: 4000 m / 13100 ft
Range: 1000 km / 621 miles
Armament: 1 x 7.7mm machine-gun, 220kg of bombs

1919 Biplane flying-boat used for the Schneider Trophy races.
Max. speed: 197 km/h / 122 mph
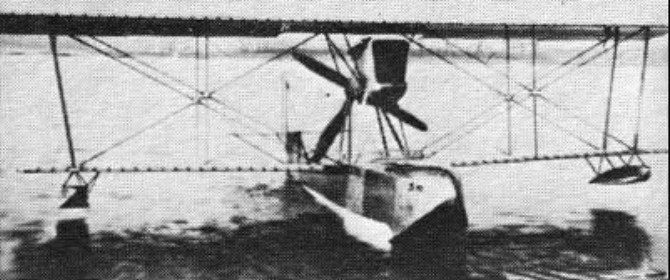
1918 Biplane flying-boat used for the Schneider Trophy races.
Max. speed: 222 km/h / 138 mph

The S.8 was a reconnaissance and anti-submarine two-seat biplane flying-boat of 1917, powered by a 126kW Isotta-Fraschini I.F.V-4B or 89kW Colombo F-150 engine mounted in pusher configuration. A total of 172 was produced for the Italian Navy.
Max take-off weight: 1375 kg / 3031 lb
Empty weight: 900 kg / 1984 lb
Wingspan: 12.77 m / 42 ft 11 in
Length: 9.84 m / 32 ft 3 in
Height: 3.3 m / 11 ft 10 in
Wing area: 46 sq.m / 495.14 sq ft
Max. speed: 144 km/h / 89 mph
Ceiling: 6000 m / 19700 ft
Range: 700 km / 435 miles
Armament: 1 x 7.7mm machine-gun, 120kg of bombs
France
Founded at Chartres by Robert Savary. Was building biplanes in 1910. Won order for three aircraft after military trials in 1911. In February 1913 Joseph Frantz established time-to-height record on Savary biplane with Salmson engine, carrying five passengers, but prewar output was ten machines only. In 1915 Robert Savary was associated with Henri de la Fresnaye in forming a joint company to build Nieuport fighters. No aircraft built after First World War.
S. E. Ltd Saunders began own design, first of which was T.1 two-seater (1917) with detachable wings for ship-board stowage.
UK
Based at Cowes, Isle of Wight. Originally built boats, and later hulls for fast motor boats and some of earliest flying-boats (e.g. Sopwith Bat Boat). Especially famous for “Consuta” copper-sewn plywood construction.
In 1913 received order for B.E. biplanes. During First World War built under subcontract Avro 504 landplanes, Short 184 floatplanes and Norman Thompson and Felixstowe F.2A and F.5 flying-boats.
Began own design, first of which was T.1 two-seater (1917) with detachable wings for ship-board stowage. Aircraft built postwar included the Kittiwake seven-passenger twin-engined wooden amphibian of 1920 with camber-changing gear on wing leading and trailing edges; Medina ten-passenger twin-engined wooden flying-boat of 1926; and Valkyrie three-engined military flying-boat of 1927 with developed form of Linton-Hope hull.
The 1918 Curtiss Pursuit is possibly a rebuild or modification from something surplus, possibly JN-4, and OX-5 powered.
Bought by B Larsen and E E Terrell of Oakland in 1928 and registered NC471 c/n TL100sub, it was reported overhauled in 1929, and registration cancelled by CAA on 7 May 1930 for unspecified reason.
Oakland CA.
USA
Circa 1918 built the Curtiss Pursuit