The origins of aircraft construction in Turkey can be traced back to the first maintenance unit of the Turkish Air Force officially established on 1 June 1911, set up at the airport in Yesilköy / Istanbul. During the First World War maintenance facilities were established in Baghdad, Damascus, Izmir and Konya. They were under the umbrella of the 9th Department of Aviation Affairs (9 Hava Isleri Subesi), which was established on 15 Febuary 1915. The main task of this maintenance facilities was the maintenance of the aircraft of the German Air Force but due to the war situation could not always be guaranteed the supply of spare parts. The technicians at the front often no choice but to produce the items urgently needed themselves. In 1917 the Baghdad facility built a “new airplane”, the Baghdad first, which was built from parts of Albatros C III and from captured aircraft parts “redesigned”.
World War 1
Turkish Air Force
The origins of aircraft construction in Turkey can be traced back to the first maintenance unit of the Turkish Air Force officially established on 1 June 1911, set up at the airport in Yesilköy / Istanbul. During the First World War maintenance facilities were established in Baghdad, Damascus, Izmir and Konya. They were under the umbrella of the 9th Department of Aviation Affairs (9 Hava Isleri Subesi), which was established on 15 Febuary 1915. The main task of this maintenance facilities was the maintenance of the aircraft of the German Air Force but due to the war situation could not always be guaranteed the supply of spare parts. The technicians at the front often no choice but to produce the items urgently needed themselves. In 1917 the Baghdad facility built a “new airplane”, the Baghdad first, which was built from parts of Albatros C III and from captured aircraft parts “redesigned”. During the Liberation War, which began immediately after the end of the First World War, the need for a separate aircraft production became increasingly clear.
The first steps for national aircraft production were initiated. Firstly reconstructions were performed on available aircraft types on the Gaziemir / Izmir Air Force Base. In 1922 two captured Airco DH 9 were retrofitted with dual controls. In 1924, the unreliable original engines were replaced on four B.1 Aviatik SAML training aircraft with older, but proven, Mercedes engines.
Turkish aircraft in the true sense began only after the founding of the Republic in 1923. A small delegation was dispatched to Europe to procure aircraft for the new Turkish Air Force. After evaluation it was decided to obtain 16 Bréguet XIV A-2, 39 Caudron C-27 and 32 Caudron C-59 aircraft. These aircraft were dismantled in 1924 and shipped to the Gaziemir / Izmir Air Force Base under French supervision. After the first requirements of the Turkish Air Force, the armed force withdrew from the assembly of planes however, this plan did not last long. When in the course of technical development, the maintenance became more complicated and more complex, the maintenance facilities of these forces were again entrusted with the manufacture of spare parts or installation or modernization of aircraft. So the 1st Air Supply and Maintenance Center emerged (1 Ikmal Hava ve Bakim Merkezi, 1.HIBM) in Eskisehir (1926), the 901 Home Depot and production plant for aircraft (the 901.Hava Araci Ana Depo ve Fabrika Komutanligi, nine hundred and first HAADFK) in Polatlı (1948, 1962 in Ankara) and the 2nd Air Supply and Maintenance Center (2nd Hava Ikmal ve Bakim Merkezi, 2.HIBM) in Kayseri (1950).
Tummelissa TU-1
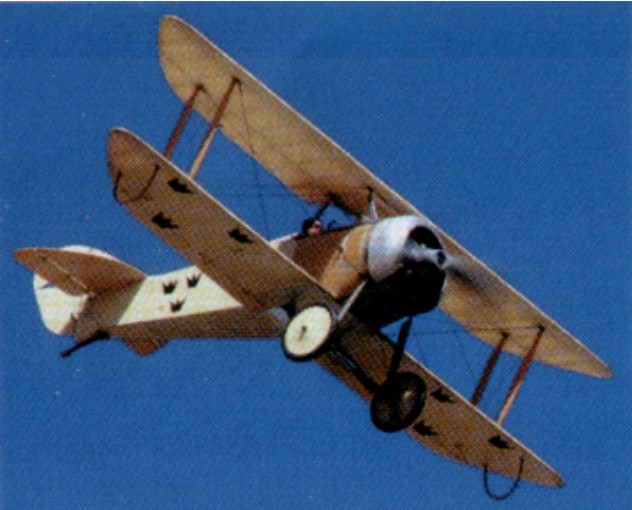
Designed and built by the Swedish Army Aircraft Factory, as a trainer for the Swedish airforce and first flown in June 1919. Only 28 were built before the type was retired in the 1920s.
Engine: Thulin A rotary
Timm Aircraft Corp
Several experimental planes were produced during 1911-20, but data are lacking. Company logo proclaims 1911 as starting year.
Formed at Van Nuys, California, USA, circa 1922 as the O W (Otto William) Timm Aircraft Corp,
901 N San Fernando Rd, Glendale CA.
c.: 1928: Timm Airplane Co.
Was inactive in aircraft manufacture for several years, but in late 1930s produced prototype T-840 twin-engined six-seat transport.
1935: Timm Aircraft Co.
1937: Acquired Kinner Aircraft
1939: Metropolitan Airport, Van Nuys CA.
It developed a plastic-bonded plywood Aeromold, applying this first to the S-160-K two-seat primary trainer of 1940, which was built in Second World War as N2T-1 trainer for U.S. Navy.
Timm also built 434 Waco CG-4A cargo gliders, and did wartime subcontract work for Harlow, Lockheed, Vultee and other companies.
1941: Sold to Aetna Aircraft Corp, Los Angeles.
Charles Lindbergh’s first airplane ride was with barnstormer Timm.
AB Enoch Thulins Aeroplanfabrik (AETA)

Title from 1914 of the former AVIS (Aeroplanvarvet i Skane) company formed 1913 by Dr Enoch Thulin and Oskar Ask. Licence built Le Rhone engines.
Models A, B, C and D were respectively Swedish versions of the Bleriot monoplane, Morane-Saulnier monoplane, Albatros B.II and Morane-Saulnier parasol. Thulin designs included the Type E, FA, G, GA, H, K, L, LA, N and NA. Total factory output was 99 aircraft, of which 32 produced in 1918. By the end of 1918 had produced nearly 100 aircraft of 11 different types, 7 their own design.
Dr Thulin died in flying accident in 1919 and the company closed its doors lacking the leadership of the early pioneer. ABThulinverken, a company which was formed a year later, is not connected with aviation.
Thompson-Day

The 1914 Thompson-Day was designed by D L Thompson and C H Day as a two-place open cockpit biplane powered by a 90hp Gyro Duplex.
It set altitude record of 15,580′ in 1914. Thompson was also often photographed flying this plane in competition with race cars.
Thompson 1915 Biplane

Built by Charles H Day at Griffith Park, Los Angeles CA., the 1915 Thompson Biplane was powered by an 80 hp rotary engine. Thompson had been looping the plane successfully.

Thompson, De Lloyd
Cicero IL
USA
Circa 1914-15 airplane builder
Thomas-Morse SH-4
The 1915 Thomas-Morse SH-4 was a USN float version of the Thomas T-2 with a single main pontoon and wingtip floats, larger tail, three-bay wings, and various engines including the Curtiss OX-5 and Hisso A.
The first design for Thomas-Morse by B D Thomas, it incorporated much of the same look as his Curtiss J, and sold for $7,575.
Fifteen were built; A134 to 136, and A395 to 406.
Wingspan: 44’0″
Length: 29’9″
Useful load: 897 lb
Speed: 83 mph
Thomas-Morse MB-2

The sole Thomas-Morse MB-2 AS25806 of 1918 was powered with a 400hp Liberty 12-C but refitted with 450hp Liberty and four-bladed prop. It still lacked performance and it is not recorded if it ever completed flight tests.
Engine: 400hp Liberty 12-C
Wingspan: 31’0″
Length: 24’0″
Useful load: 726 lb
Seats: 2