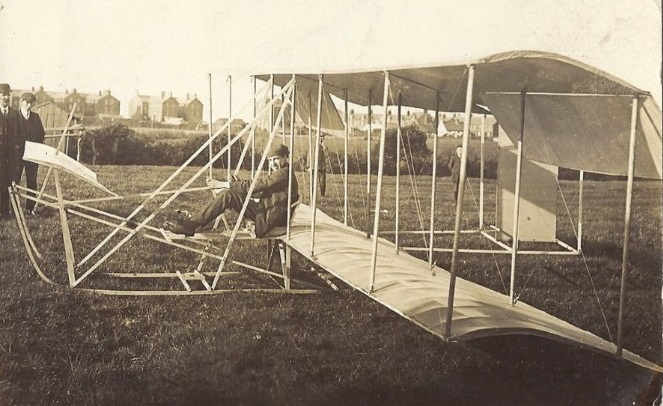

In 1912 Fred Woods built a Wright type biplane glider at Fleetwood, UK.

In 1912 Fred Woods built a Wright type biplane glider at Fleetwood, UK.

Equipped with a 40 hp ABC inline four, built by Tsoe K. Wong. Designed and built in the UK in 1913, and initially flown there, the craft was later shipped to Kuala Lumpur, in what was then known as the Federated Malay States. The craft met its end on July 19 1914, due to a demo flight that concluded with a fairly emphatic crash.
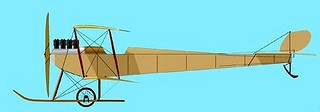
The Wolverine Aeronautic Co, Albion MI., USA circa 1911 was a supplier of home-builders’ kits and materials. They featured two open cockpit biplane models with 25hp (span: 26’0″) and 30hp (span: 30’0″), powered by Wolverine’s own-brand motor.
One machine was reported by Aeronautics to have been built for the Chinese revolutionary party, representatives of which watched it in demonstration at Hempstead, but that “apparently the idea of using aeroplanes was given up at the time.”
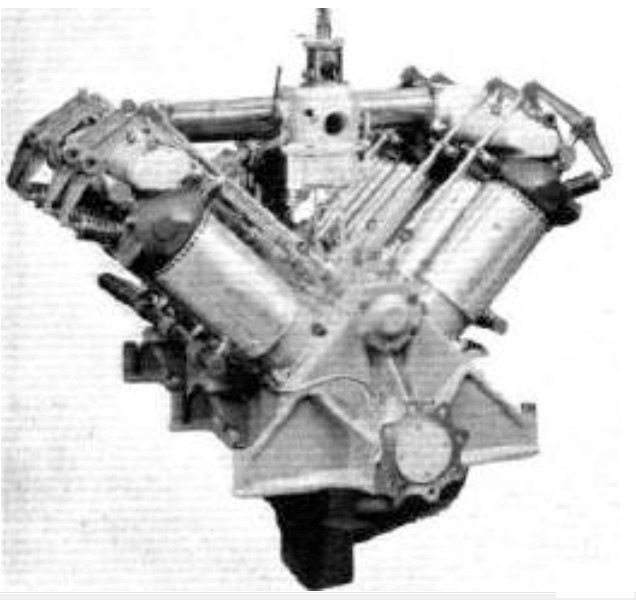

The Wolseley 160 hp was a British V-8, water-cooled aero engine that first ran in 1910, it was designed and built by Wolseley Motors. Its sole known use was in the ill-fated HMA No. 1 airship which broke in two while being removed from its shed on 24 September 1911.
160 hp
Type: eight-cylinder, 90 degree, upright V-engine
Bore: 5.0 in (127 mm)
Stroke: 7.0 in (178 mm)
Displacement: 1,100 cu in (18 L)
Fuel type: Petrol
Cooling system: Water-cooled
Reduction gear: Direct drive, right-hand tractor
Power output: 147 hp (110 kW) at 1,200 rpm (maximum power for “short periods”)
Specific power: 0.13 hp/cu in (6.1 kw/L)

A glider of Lilienthal type but with a landing ski, built by Ingenieur Alois Wolfmüller from München, Germany, and datable to April 1908. It was a modification of a 1907 biplane glider, modified to monoplane configuration.
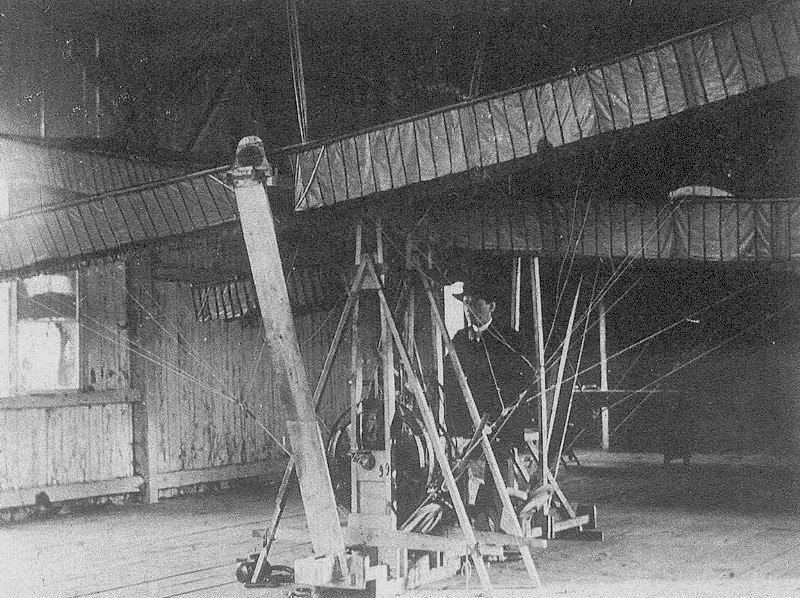
Alois Wolfmüller’s “Schlagflügelapparatur”, or “Standflugmaschine”, dated from December 1901. Powered by an 18 hp three-cylinder engine of Wolfmüller’s own design, the ornithopter with three wings in tandem arrangement was apparently able to rise 60 cm off the floor, but was very unstable. It was inspired by an 1868 test-rig of his friend Otto Lilienthal.
Alois Wolfmüller was born in Landsberg am Lech. Together with Heinrich and Wilhelm Hildebrand he developed the 1894 Hildebrand & Wolfmüller motorcycle, the first in the world to be produced in series.
Wolfmüller’s “Schlagflügelapparatur”, or “Standflugmaschine” ornithopter, dated from December 1901.

The invention of Dr. Karl Wölfert; an 800 cubic meter capacity non-rigid dirigible, driven by an internal combustion Daimler gasoline motor of 8 hp. Wölfert made ascensions on “Deutschland” at Tempelhof-Berlin on August 28 and 29, 1896 and on March 6, 1897, but did not have a lot of success navigating his machine. On June 12, 1897, an exhibition of “Deutschland” in front of government dignitaries and military men ended disastrously. Carrying Dr. Wölfert and his mechanic Robert Knabe, the airship rose to 200 meters and was suddenly engulfed in flame, dashing both men to their death. The airship was the first to have an accident involving the combustion of the hydrogen lift gas resulting in fatalities.
In 1880, Karl Wölfert and Ernst Georg August Baumgarten attempted to fly a powered airship in free flight, but crashed.
In 1888, Wölfert flew a Daimler-built petrol engine powered airship “Deutschland” at Seelburg.

Triplane duo-seat glider designed and built in 1909 by Carl Wolf and August Becher, variously described as being from Oakland, California or Fitchberg, California. The aircraft is said to have made flights of up to 200 feet when launched from a specially built inclined ramp, 50 feet in height.
Wingspan: 19′ 8″
Wing area: 220 sq ft