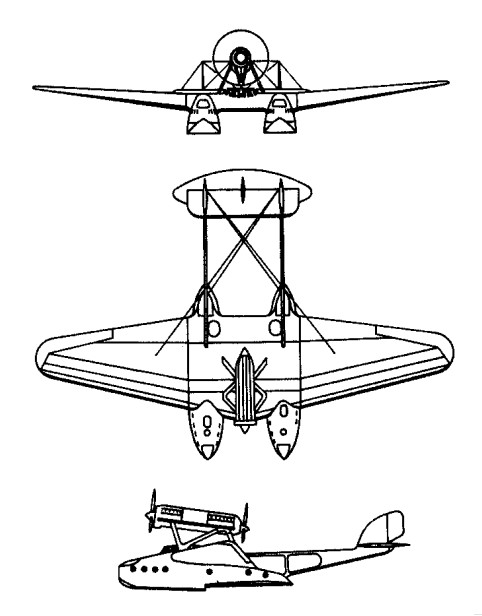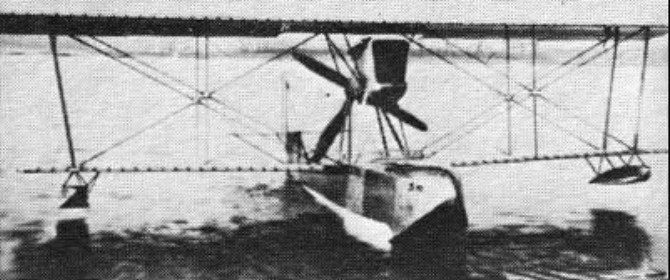
The Savoia-Marchetti S.56 of 1924, a three-seat trainer/tourer flying-boat, was an unequal-span biplane mainly of wooden construction. Pilot and co-pilot were seated side-by-side in separate cockpits equipped with dual controls, a third cockpit being located just behind them. Power was provided by a 52kW Anzani engine, but two S.56A boats built with 60kW Anzanis had a slight increase in wing span and were given amphibious capability by the introduction of manually-retracted wheel landing gear.
At least 12 S.56As were sold to private owners and clubs and four were used by the Regia Aeronautica for training; they were powered by a variety of engines, including the 86kW Fiat A.53, 101kW Fiat A.54, and Walter Venus radials.

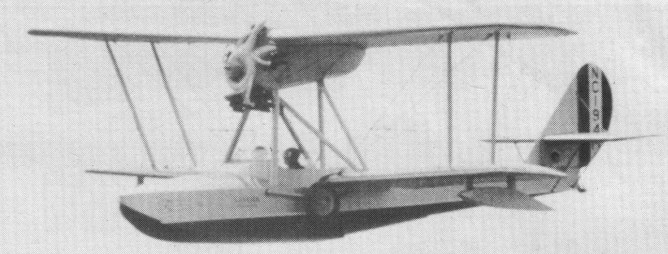
The American Aeronautical Corporation began licence-production of the three place S.56 in 1929 (ATC 287), powered by the 90 hp / 67kW Kinner K5 engine, and three two-seat machines were followed by at least 40 three-seater.
American Aeronautical Corp built an all-stainless-steel version of Savoia Marchetti S-56 powered by a 210hp Kinner, NX749N. It was exported to Italy.
The S-56 selling for $7,375 with starter and nav lights. Twenty-five were built on Long Island, New York including NC192/194M, NC324N/325N, NC349N, NC352N/356N, NC371N, NC378N, NC380N, NC382N/383N, NR898W, NC900V/906V, and NC908V, of which three were converted to S-56-B (ATC 2-95) and one to S-56-C (ATC 2-96) for initial production models.

In 1930 the S.56B, powered by a 93kW Kinner B5, was flown in the USA. Sellong for $7,875, ten were built including NC67K, NC324N, NC351N, NC356N, NC386N, NC858W, NC898W, NC897V, NC900V, and NC906V, of which three were converted to S-56-31 (2-332) for two two-place modifications. One was built with an enclosed cockpit canopy and one, converted to single-seat capacity, with additional fuel tanks and redesignated S.56C, was used on a round-the-world trip by American businessman Zachery Reynolds.

American Aeronautical Corp S-56-C, or S-56-31 conversions in 1930 were NC67K, NC858W, and NC898W plus NC14381 which wore an out-of-sequence c/n 55, with 100hp Kinner engines.
An all-metal version of the S.56 was built by the American Edwin Budd Corporation in 1932 and designated Budd BB-1.
S.56A
Max take-off weight: 975 kg / 2150 lb
Wingspan: 10.72 m / 35 ft 2 in
Length: 7.8 m / 26 ft 7 in
Height: 2.99 m / 10 ft 10 in
Wing area: 26.5 sq.m / 285.24 sq ft
Max. speed: 138 km/h / 86 mph
Ceiling: 1670 m / 5500 ft
American Aeronautical Corp S-56
Engine: Kinner K-5, 90hp
Wingspan: 34’1″
Length: 25’0″
Useful load: 699 lb
Max speed: 86 mph
Cruise speed: 75 mph
Stall: 40 mph
Range: 290 mi
Ceiling: 7000 ft
Seats: 3
American Marchetti S-56, BB-1 / American Aeronautical Corp S-56-B
1926
Engine: Kinner B-5, 125hp
Prop: 2 blade wooden fixed pitch
Wingspan: 31 ft 1 in
Length: 25 ft 7 in
Wing area: 285 sq.ft
Empty weight: 1350 lb
Loaded weight: 2150 lb
Useful load: 738 lb
Max speed: 95 mph
Cruise: 80 mph
Stall: 40 mph
Ceiling: 7000 ft
Range: 280 mi
2-3 seat civil transport/trainer
36-40 built in the USA
American Aeronautical Corp S-56-C / S-56-31
Engine: Kinner, 100hp