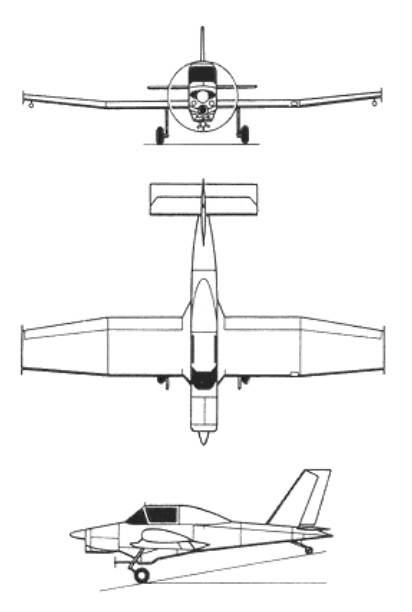
Design of an agricultural aircraft, to a specification laid down by the Brazilian Ministry of Agriculture, was initiated in May 1969 by the Departmento de Aeronaves of the nation’s Centra Te’chnico de Aeronautica. Following the establishment of EMBRAER on 2 January 1970, responsibility was transferred to EMBRAER.
The first prototype, registration PP-ZIP, was flown for the first time on 31 July 1970, at Embraer’s headquarters in São José dos Campos, State of São Paulo.
Designated originally EMBRAER EMB-200 Ipanema (the name was chosen in honor of the Ipanema farm, located in Iperó, 128 km (80 miles) far from the city of São Paulo), the aircraft was a cantilever low-wing monoplane of all-metal construction with fixed tailwheel landing gear and power provided by a 260 hp / 194kW Avco Lycoming O-540-H2B5D engine, fixed-pitch propeller, hydraulic spraying system, and a 580 liter hopper.
Brazilian type certification was gained on 14 December 1971 and initial production versions were the EMB-200 and EMB-200A which differed by having fixed-pitch and variable-pitch propellers respectively. The Corsário de Aviação company from the State of Goiás, ordered ten aircraft, in March 1971, and was the Ipanema’s first customer. In February 1972, the first airplane, registration number PT-GBA, was delivered and entered service in the fight against pests that threatened cotton crops.
In 1974, after 73 EMB-200 series aircraft had been built, production of an improved EMB-201 began; this latter differed by having a 224kW IO-540 engine with a constant-speed propeller and detail improvements.
In November 1973, the 100th airplane was delivered to Serviços Agro Aéreos do Sul. In 1975, Uruguay’s Ministry of Agriculture and Fishing ordered ten Ipanemas, along with five EMB 110 Bandeirantes, marking Embraer’s first exports. A total of 200 EMB-201s was built.
In 1977, the updated EMB-201A first flown on 10 March, entered production. This introduced a new wing profile, improved systems and revisions in cockpit layout.
In 1980, Embraer acquired Indústria Aeronáutica Neiva, a company founded in 1954 and that produced small airplanes. With the merger of the two companies, the Ipanema’s production was transferred to Botucatu, São Paulo, in 1982. A total of 355 had been ordered by 1990, bringing total Ipanema sales to more than 630. In 1988, by which time 600 had been delivered, a further improved Ipanema was launched, but without a new designation, and options include a three-bladed Hartzell propeller, larger wheels, more powerful 300 HP engine, tail wheel with a larger diameter, new shock absorbers and wing profile, among others.
The EMB-201R is a single-seat glider-tug aircraft for the Brazilian Air Force. Three were built for the Air Force Academy gliding club. Brazilian Air Force designation U-19.
Certified in November 2015, the EMB-203 with a 320 hp Lycoming engine, has a wingspan of 13.3 m and its winglets redesigned, increasing control and improving the efficiency of spraying.
By August 2010, the Ipanema is the leader of Brazil’s agricultural aviation, with more than 1,100 planes delivered and 75% of the fleet in operation, nationwide.
On 15 March 2005, the 1000th Ipanema was delivered. Coincidentally, that was also the first model with the 320 HP ethanol-powered engine, which is the same fuel developed in Brazil used mainly by the nation’s automobiles. The project was developed in a partnership with the Department of Aerospace Science and Technology (Departamento de Ciência e Tecnologia Aeroespacial – CTA). From that point on, Embraer began to offer ethanol conversion kits for the airplanes powered by aviation gasoline (AvGas). Currently, around 25% of the Brazilian fleet uses ethanol.
Gallery
EMB-200
Engine; 1 x Avco Lycoming IO-540-H2B5D, 260hp
Wingspan: 36 ft 9 in / 11.20 m
Length: 24 ft 4.5 in / 7.43 m
Max payload norm: 1212 lb / 550 kg
Max payload restricted: 3963 lb / 1800 kg
Cruise 67%: 114 kt / 131 mph / 211 kph
ROC SL: 705 fpm / 215 m/min
Max range: 507 nm / 584 mi / 941 km
Seats: 1
Hopper capacity: 149.5 ImpG / 680 lt
Cockpit length: 3 ft 11.25 in / 1.20 m
Cabin width: 2 ft 9.5 in / 0.85 m
Cabin height: 4 ft 4.5 in / 1.34 m
EMB-200A
Prop: CS VP
EMB-201
Engine; 1 x Avco Lycoming IO-540-K1D5, 300hp / 224kW
Prop: CS VP
EMB-201A
Engine; 1 x Avco Lycoming IO-540-K1J5D, 300hp / 224kW
Max take-off weight; 1800 kg / 3968 lb
Empty weight; 1011 kg / 2229 lb
Wingspan; 11.20 m / 36 ft 9 in
Length; 7.43 m / 24 ft 5 in
Height; 2.22 m / 7 ft 3 in
Wing area; 19.94 sq.m / 214.63 sq ft
Max. speed; 225 km/h / 140 mph
Cruise speed; 204 km/h / 127 mph
Ceiling; 3470 m / 11400 ft
Range; 877 km / 545 miles
EMB-202
Powerplant: 1 × Textron Lycoming IO-540-K1J5D, 224 kW (300 hp)
Wingspan: 11.69 m (38 ft 4 in)
Length: 7.43 m (24 ft 5 in) (tail up)
Height: 2.20 m (7 ft 3 in) (tail down)
Wing area: 19.94 m2 (214.6 sq ft)
Aspect ratio: 6.9:1
Empty weight: 1,020 kg (2,249 lb)
Max takeoff weight: 1,800 kg (3,968 lb) (restricted category)
Fuel capacity: 264 litres (70 US gal; 58 imp gal) usable fuel
Hopper capacity: 950 litres (250 US gal; 210 imp gal) liquid or 750 kilograms (1,650 lb) dry
Maximum speed: 230 km/h (140 mph, 120 kn)
Cruise speed: 213 km/h (132 mph, 115 kn) (75% power)
Stall speed: 92 km/h (57 mph, 50 kn) (power off)
Never exceed speed: 272 km/h (169 mph, 147 kn)
Range: 938 km (583 mi, 506 nmi)
Service ceiling: 3,470 m (11,380 ft)
Rate of climb: 4.7 m/s (930 ft/min)
Take-off run to 15 m (50 ft): 332 metres (1,089 ft)
Landing run from 15 m (50 ft): 412 metres (1,352 ft)
Crew: 1 pilot
EMB-203
Engine: 320 hp Lycoming
Wingspan: 13.3 m