The aircraft was designed by engineer Eugeniusz Stankiewicz, being a teacher in the Aviation School in Zamość. Works started in late 1944, soon after the liberation of eastern Poland, when central and western parts were still occupied by the Germans. The design of a trainer and liaison plane was approved by the Polish military Aviation Command, and Stankiewicz completed documentation in an aircraft factory PZL-Mielec in Mielec (the factory was destroyed by the Germans and at that time existed as repair works only).
There, a prototype was built, utilizing parts of the Soviet Polikarpov Po-2, like an engine with a propeller, wheels and seats, also a construction of a fuselage was similar to the Po-2. The plane, named S-1 (for Stankiewicz), was very simple.
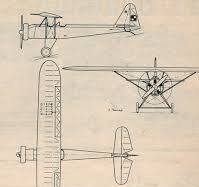
Wooden construction braced high-wing (parasol wing) monoplane, conventional in layout. Fuselage built of a frame, plywood and canvas covered. Rectangular wing with rounded tips, two-spar. Crew of two, sitting in tandem, in open cockpits with windshields. Fixed conventional landing gear, with a rear skid. Radial engine M-11D in front, with a Townend ring, two-blade wooden propeller (2.4 m diameter). Fuel tanks 126 L.
It was flown on 15 November 1945, by the Soviet pilot Piotr Kondratyenko. It was the second Polish-designed plane, that flew after the war (the first was LWD Szpak). Further aircraft were not produced.
The prototype crashed on 14 May 1946 in Warsaw in a bad weather, however its pilot, who was Stankiewicz himself, survived.
Powerplant: 1 × Shvetsov M-11F, 93 kW (125 hp)
Propeller: 2-bladed fixed-pitch
Wingspan: 13 m (42 ft 8 in)
Wing area: 20 m2 (220 sq ft)
Length: 8.5 m (27 ft 11 in)
Height: 3.2 m (10 ft 6 in)
Empty weight: 700 kg (1,543 lb)
Gross weight: 1200 kg (2,640 lb)
Wing loading: 60 kg/m2 (12 lb/sq ft)
Maximum speed: 180 km/h (110 mph, 97 kn)
Stall speed: 55 km/h (34 mph, 30 kn)
Range: 600 km (370 mi, 320 nmi)
Service ceiling: 3,800 m (12,500 ft)
Rate of climb: 3 m/s (590 ft/min)
Crew: 2