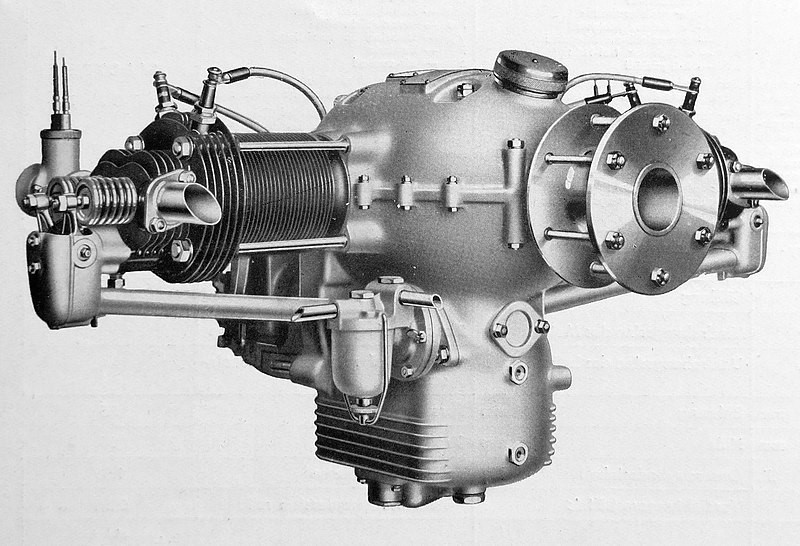
Designed by František Adolf Barvitius in 1934, the Walter Atom was an air-cooled horizontal (flat) two-cylinder engine used on light aircraft and gliders.
It was the smallest engine in the Walter air-cooled range built between the world wars, and was markedly atypical in that it was a flat, horizontal engine. It was originally intended as a suitable power unit for motorized gliders. It is also interesting that on the “eve” of World War II, amateur pilots in Aeroclubs began to use motorized gliders. Pavel Beneš counted on it for the first such glider (Be-500 “Bibi”) from the Beneš-Mráz aircraft factory in Choceň, Pavel Beneš – Jaroslav Mráz. However, this plan was not implemented, but the design preparation of the type Beneš-Mráz Be-500 Bibi was used in the construction of subsequent types Be-501 and Be-502. However, they used more powerful Walter Mikron and Walter Minor 4 engines.
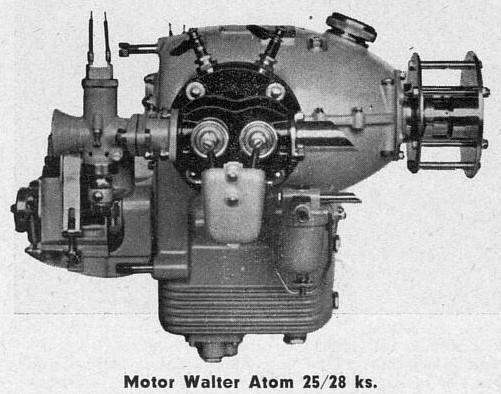
The two-piece motor housing was cast from Hiduminium and was closed on both sides with electron lids. Ribbed aluminum alloy heads with bronze seats and valve guides were mounted on the ribbed steel cylinders. The cylinder heads were removable and were attached to the housing along with the cylinders by four through bolts. The head and the cylinder itself were surface protected by galvanic cadmium plating.
The steel crankshaft was made of machined forging and was housed in a housing in two bronze plain bearings, which were cast with bearing metal, and in one pressure ball bearing, which absorbed the axial forces from the propeller. The propeller head was mounted on the tapered end of the crankshaft and was secured with a wedge and nut. The H-section connecting rods were forged from aluminum and the pistons were cast. The pistons had two sealing rings and one wiper ring. The lubrication was a pressure circulating (wheel pump) with an oil tank at the bottom of the engine case.
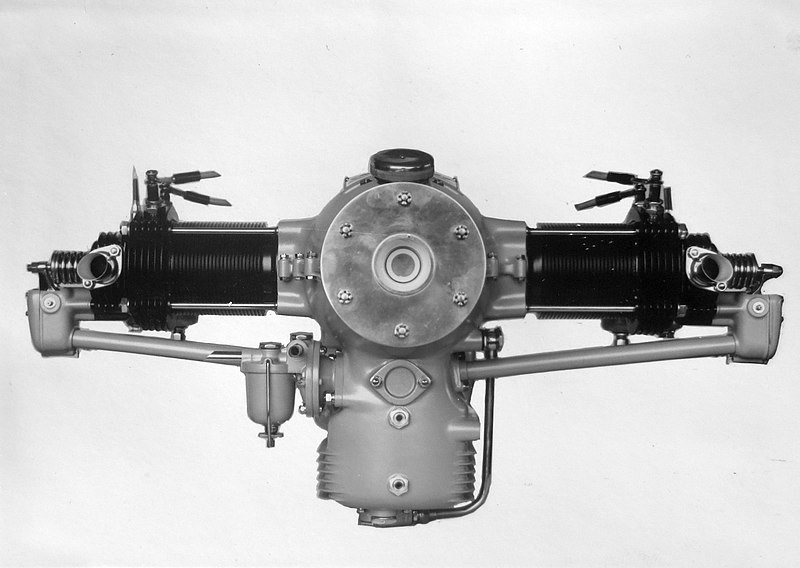
There was one Amal carburetor with a corrector on each cylinder. The ignition was double, Bosch-type magnets that were mounted on the rear bonnet.
The Walter Atom engine was created in 1934, went into small-scale production in 1935 and reached a maximum take-off power of 20 kW (28 hp), which in turn was not so small for a two-cylinder with a capacity of 1.1 liters. The arrangement of the engine with the cylinders facing each other was chosen so that the operation of the engine did not strain the construction of the machine (aircraft, glider).
The Atom was manufactured by Walter Joint-Stock Company, a car and aircraft engine factory, since 1935.
In April 1936, the MLL sail department at Walter built the ŠP2 glider, on which the two-cylinder Atom was to be mounted. However, the main application was the conversion of the classic glider EL-2-M “Gray Wolf” to a motorized version. The designation was created as standard: EL are the initials of the designer (Elsnic Ludvík) and 2-M means two-digit. According to other sources, the “M” in the designation referred to the possibility of mounting the engine on a glider.
The first motorized Gray Wolf (EL-2-M) was a glider built by the sailing department of the Masaryk Aviation League (MLL) in Moravian Ostrava. The new Walter Atom engine from 1935 was used here for the first time. The engine was on a tubular pyramid above the canopy of a wing with a propeller. It was mainly used as a two-seater for training students of gliding who have already passed the “B” exam.
Enthusiasts from the active branch of the Masaryk Aviation League (MLL) in Humpolec are behind the most well-known application on a motorized glider. At the beginning of 1937, they built a motorized, single-seater glider, which was actually a slightly redesigned school two-seater glider EL-2-M Gray Wolf with an auxiliary engine Walter Atom. The designer of the Gray Wolf, Ludvík Elsnic, the chief pilot of the MLL, flew and tested this modified glider on April 11, 1937.

The numbers of engines produced 1935-1939 are not reported in official sources, apparently only as units.
After the Second World War, a similar, small engine, in-line two-cylinder Walter A (type designation M-100) designed by Bohuslav Šimůnek (1946) was created in the Walter factory. It had a rated power of 16 kW / 22 hp at 2,500 rpm and was also designed to power motorized gliders.
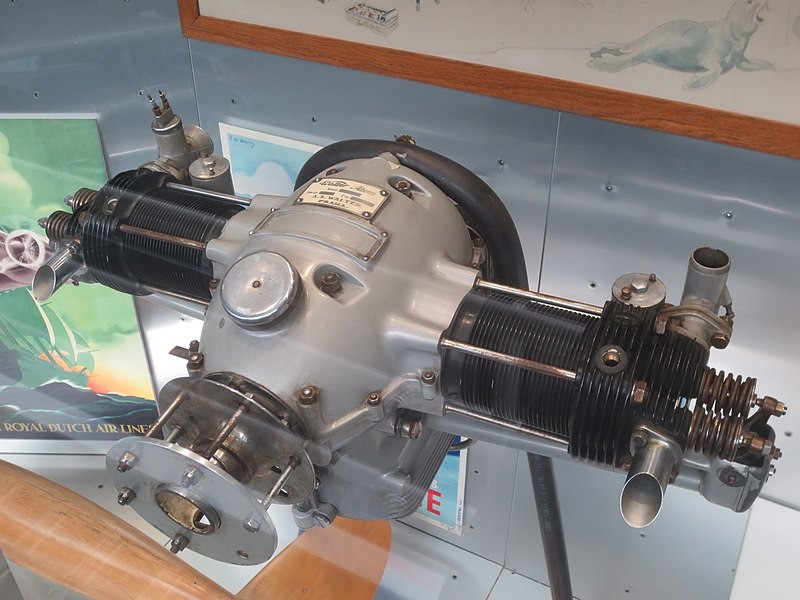
In the National Technical Museum, a preserved Walter Atom engine is on display in the transport hall.
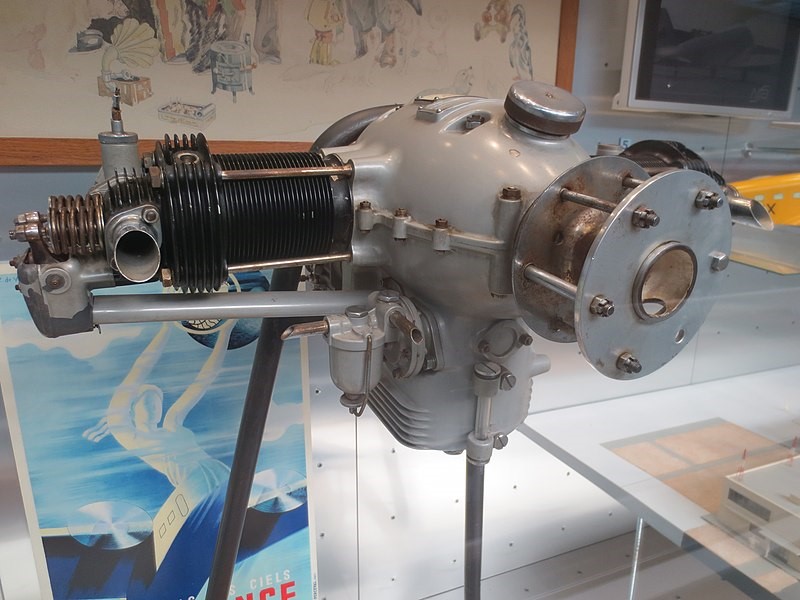
Atom
Type: Horizontal 2 cylinder air-cooled
Bore: 85 mm (3.35 in)
Stroke: 96 mm (3.78 in)
Displacement: 1.09 L (66.5 cu in)
Total piston area: 437 cm²
Length: 510 mm (20.08 in)
Width: 815 mm (32.09 in)
Height: 409 mm (16.10 in)
Dry weight: 40 kg (88.2 lb)
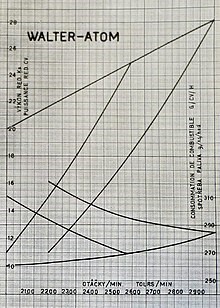
Nominal, rated power: 25 hp (18.4 kW) at 2600 rpm
Maximum (take-off) power: 28 hp (20.6 kW) at 3000 rpm
Power / volume ratio: 22.7 k / l (16.7 kW / l)
Valvetrain: 1 inlet and one exhaust valve per cylinder
Lubrication: pressure, circulating
Oil consumption: 15–20 g · h − 1 · k − 1 / 20.4-27.2 g · h − 1 · kW − 1
Fuel system: 2 Amal carburettors
Fuel type: 68 octane
Fuel consumption: 260–270 g · h − 1 · k − 1 / 354–367 g · h − 1 · kW − 1
Cooling system: air
Distribution: OHV, one intake and one exhaust valve per cylinder
Ignition: 2 Bosch magnets
Power output: 21 kW (28 hp) at 3000 RPM
Compression ratio: 5.2:1
Power-to-weight ratio: 2.14 kg/kW (3.52 lb/hp) at cruise
Power to weight ratio (specific weight): 0.62 k / kg (0.46 kW / kg)
Specific performance: 1.6 kg / k (2.14 kg / kW)