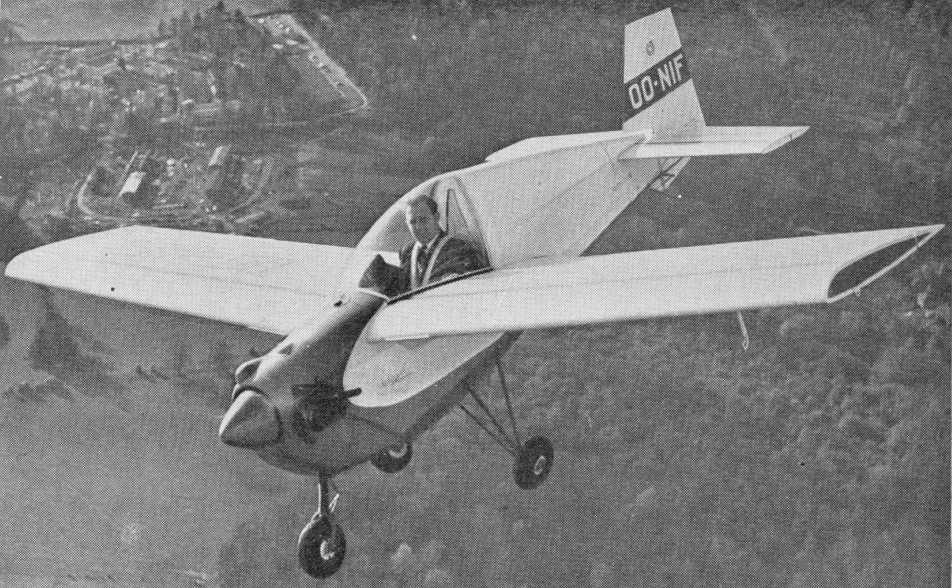
Conceived by Ernest Oscar Tips, managing director of Avions Fairey SA, and produced by Tipsy intended primarily for manufacture in kit form. The Nipper flew for the first time on 2 December 1957, powered by a 40 hp Pollmann HEP engine, entering production as the T.66 Mk.1. The first production model flyng on 10 March 1959.
Identical to the Mk.1 apart from its 45 hp Start Stamo 1400A engine, the Mk.2 first flew on 16 February 1959. Nipper production by Avions Fairey commenced almost immediately and the first production T66 Mk.II, flew on 20 October 1959.
Avions Fairey produced the Nipper in both fly-away and kit forms, the latter aimed at the developing amateur constructor market. However, it is not known how many units the company built. Construction numbers which are usually a reliable indication of production figures suggest at least eighty Nippers came off the company’s Gosselies production line before manufacturing rights were transferred to Coblevia in 1961, another Belgium company. Coblevia, after some design changes, produced aircraft marketed as the Coblevia Nipper III.

In June 1966 manufacturing rights to the Nipper were purchased by an English company Nipper Aircraft Ltd and a deal was negotiated with Slingsby to produce the aircraft at its Kirbymoorside glider factory. These aircraft were marketed by Nipper Aircraft in three vanants. The Nipper Mk.III powered by a 1500cc Rollason Ardem (converted VW auto engine), the Mk.IIIA fitted with a 1600cc Rollason Ardem and the Mk.IIIB kitset intended for amateur construction.
Thirty-three Nippers were produced by Slingsby before production ceased toward the end of 1969.
Acro Engines and Aeroframes, the company run by contest pilot Barry Smith, using his own Volkswagen engine conversion, with fuel injection and inverted fuel and oil systems, aerobats a relatively old lightweight design, the Tipsy Nipper.
After liquidation of Nipper Aircraft in May 1971 Nipper Kits and Components Ltd. was formed to support existing aircraft, and continued to market the aircraft in Mk III form as plans and some components. In 1998 the Nipper was still being marketed by Nipper Kits & Components.

Nipper Mk.I
Engine: Pollman HEPU, 40 hp
Wing span: 19 ft 8 in
Length: 15 ft 0 in
Height: 6 ft 2 in
Wing area: 80.7 sq.ft
Nipper Mk.II
Engine: Stark Stamo 1400A, 45 hp
Wing span: 19 ft 8 in
Length: 15 ft 0 in
Height: 6 ft 2 in
Wing area: 80.7 sq.ft
Empty weight: 412 lb
Loaded weight: 660 lb
Max speed: 101 mph
Max cruise: 93 mph
Econ cruise: 84 mph
ROC: 630 fpm
Service ceiling: 13,100 ft
Range: 200 mi
Nipper Mk.III
Engine: Stark Stamo 1400A, 45 hp
Nipper Mk.III
Engine: Ardem X, 45 hp
Wingspan: 19 ft 8 in / 6.00 m
Wingspan over tip tanks: 20 ft 6 in / 6.25 m
Length: 15 ft 0 in / 4.56 m
Empty weight: 465 lb / 210 kg
MTOW normal: 750 lb / 340 kg
MTOW aerobatic: 685 lb / 310 kg
Cruise 75% no tanks SL: 81 kt / 93 mph / 150 kph
ROC SL: 650 fpm / 198 m/min
Service ceiling: 12,000 ft / 3660 m
Range internal fuel 30min res: 173 nm / 200 mi / 320 km
Range w/tip tanks: 390 nm / 450 mi / 720 km
Seats: 1
Nipper Mk.IIIA
Engine: Ardem 1600cc, 55 hp
Nipper Mk.IIIB
Empty weight: 211 kg
Wing area: 7.50 sq.m
Fuel capacity: 34 lt
Engine: VW, 60 hp
MAUW: 340 kg
Seats: 1
Max speed: 235 kph
Cruise speed: 150 kph
Minimum speed: 61 kph
Climb rate: 3.3 m/s
Fuel consumption: 12.5 lt/hr
Plan price (1998): £55
Kit price (1998): £4004
Nipper Mk.IV
Engine: Jabiru
Engine: VW
Span: 19ft 8in
Wing area: 80.75 sq.ft
Length: 15 ft
Max wt: 750 lbs
Empty wt: 465 lbs
ROC: 650 fpm
Cruise: 80 kts
Seats: 1