After finishing his studies at the VS Air Fleet Academy, Vaxmistrov went on to work at the NII VVS, where he developed his composite aircraft projects known as “Zvenó”. Upon completion of AA studies, Dubrovin went on to work at Factory No. 39 in Moscow and later as principal builder at Factory No. 301 in Khimki.
Tijonrarov in 1930, with the degree of military engineer of the second degree, was transferred to the TsKB of Factory No.39 Menzhinski where he led a motorization group.
Before saying goodbye forever, this trio of aeronautical builders designed a new glider that saw the light in 1931 under the name “Skif-2” (Russian: Тихонравов / Дубровин / Вахмистров “Скиф-2”).
The main objective of the “Skif-2” was to test the Pr-652 wing profile in flight. The new wing using this profile had been designed by AA Dubrovin and BN Sherementiev in 1930.
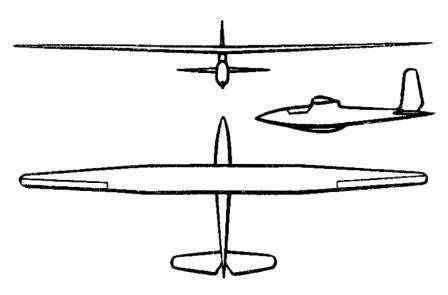
The “Skif-2” glider was designed as a single-seat monoplane with a cantilever wing in parasol. In general, it was an enlarged development of the successful “Skif”.
The structure was built in wood. The “Skif-2” incorporated a wing with double spar and wingspan increased to 17.2 meters, aspect ratio of 17.7 and a new Pr-652 profile. The wing was attached to the fuselage at three points on a central pile built as an integral part of the fuselage support structure. The centroplane had a rectangular shape and in the area where it joined the fuselage it was covered with 3 mm plywood. The wing was covered with plywood up to the position of the second spar. From then on, the covering was made of fabric.
The fuselage on the “Skif-2” remained unchanged and featured a spindle shape with a tapered bow and tail. Its structure consisted of trunk-type frames linked together by light stringers. In the rear part of the fuselage the tail unit was located was of the conventional monoplane type and in the lower part the landing ski.
The pilot was located in a closed cockpit, which had a removable celluloid cover and two small windows located at the level of the pilot’s eyes. The cockpit had so much space that the pilot could sit with his parachute. The cover provided the necessary clarity to allow the pilot to see the instrument records.
The “Skif-2” glider participated without great success in the VIII National Sailing Competitions held in Koebel . The new wing construction was 12 kg heavier than the base model, which affected the practical results of the glider. On the other hand, most of the flights were carried out without the cockpit cover, so the coefficient of aerodynamic drag rose from 0.094 to 0.115.
In general, the performance of the “Skif-2” was inferior to the “Skif”. The aerodynamic quality decreased from 22.3 to 20 and the descent speed increased from 0.7 m / s to 0.72 m / s. Due to the repair work carried out, the “Skif-2” was able to start racing late accumulating only a poor value of 20 flight hours.
Skif-2
Wingspan: 17.2 m
Wing area: 16.7 m²
Aspect ratio: 17.7
Empty weight: 200 kg
Wing loading: 16.8 kg / m²
Stabilizers surface: 2.6 m²
Elevator area: 1.24 m²
Spoiler area: 3.8 m²
Glide ratio: 20
Descent speed: 0.72 m / s
Accommodation: 1