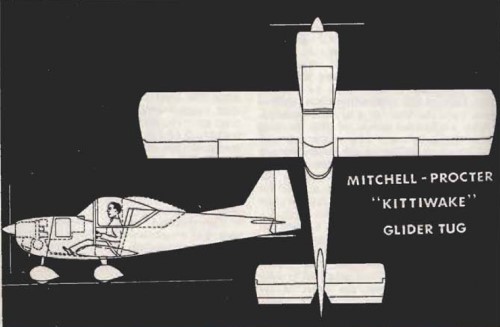
Originally designed in 1964-65 by R. G. Proctor and C. G. B. Mitchell as a dedicated single-seat glider tug aircraft. Mitchell-Procter Aircraft was set up to produce the Kittwake prototype. It was a development of the Mitchell-Prizeman Scamp design study of 1964. ‘Kit’ Mitchell was the Kittiwake’s designer, with Roy Procter in charge of building it. It had excellent visibility, sturdy landing gear.
The Kittiwake was of all-metal stressed skin construction with tricycle landing gear. The nose-wheel was steerable for taxiing and the aircraft was fitted with hydraulic brakes.

The aircraft would be capable of aerobatics with a rate of Roll 200 degrees at 103 mph (90 kn; 166 km/h). The Kittiwake had a rate of climb of 700 feet (213 metres) per minute with a 1,000 lb (454 kg) glider in tow.
The single-seat Kittiwake I is an all-metal aircraft, with low cantilever wings of parallel chord built around a single spar carrying 5° of dihedral. NACA single slotted flaps occupy the whole of the trailing edge inboard of the ailerons. The wings attach to a centre section which is integral with the fuselage, a feature intended to help construction in a small space like a garage. The straight tapered fin carries a horn balanced rudder and the constant chord tailplane has a starboard side trim tab.

The Kittiwake’s fuselage is built around four longerons, with flat sides and bottom and single curvature decking. Its overwing cockpit has a rearward sliding canopy and its fixed tricycle undercarriage has cantilever angled steel spring main legs attached to the lower longerons, giving a track of 5 ft 9 in (1.75 m). The Kittiwake I was powered by a 100 hp (75 kW) Continental O-200 engine.
The wing had generous flaps with high operating speeds which allowed for a fast descent. It had a self-starter system, provision for a radio. The Kittiwake also had a mechanism for retracting the tow rope during the descent. This design was fully aerobatic and additional fuel tanks could be fitted to extend the range.

By the middle of 1965 production tooling were being made for the wing ribs as well as spars machined.
The Kittiwake single-seat, low-wing monoplane was designed to make full use of all-metal materials and modern construction while retaining a simplicity of design that lends itself to homebuilding.

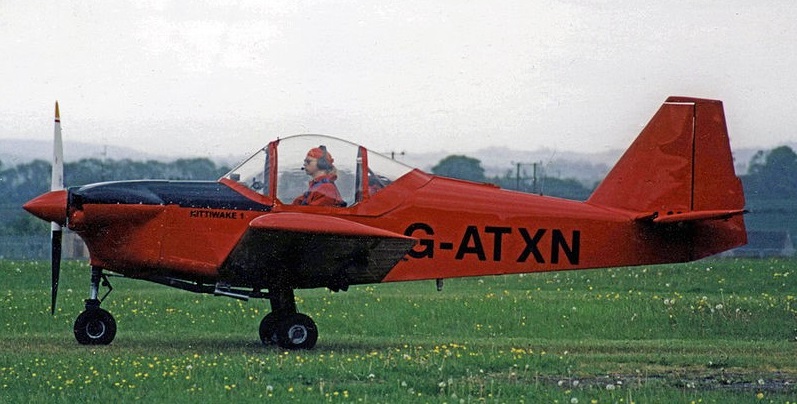
The prototype was started at Camberley but completed by BEA Engineering in 1966-7, powered by a Continental O-200-A. First flown at Lasham on 23 May 1967, it was registered G-ATXN PFA.1306. It was re-engined with a fan-cooled Lycoming O-290 at Lasham in 1972. The prototype was later known as the Mitchell-Procter Kittiwake I. Around a year and a half later the partnership was dissolved and plans for home builders were produced by Procter Aircraft Associates.
A second was built at RNAS Lee-on-Solent as an apprentice project under Lieutenant Commander Cudmore, started in 1969. First flying on 21 October 1971 sn serial XW784, at Lee-on-Solent, powered by a Rolls-Royce/Continental O-200-A.

It was subsequently registered G-BBRN. Built, one by Royal Navy apprentices in 1971 for glider towing, a larger diameter (6 ft 4 in, 1.93 m) propeller is fitted, increasing the rate of climb by 24%. A tow release hook is fitted under the tail. Only one Kittiwake II, the prototype, was built.
In later years the prototype was re-engined with a Lycoming O-290-D2 engine.
Mitchell continued development and produced the Mitchell Kittiwake II two-seater. Plans were available for both single-seat and two-seat versions, but only four were constructed. Examples built of the Kittiwake I: G-AXTN, G-BBRN (marked as XW784).
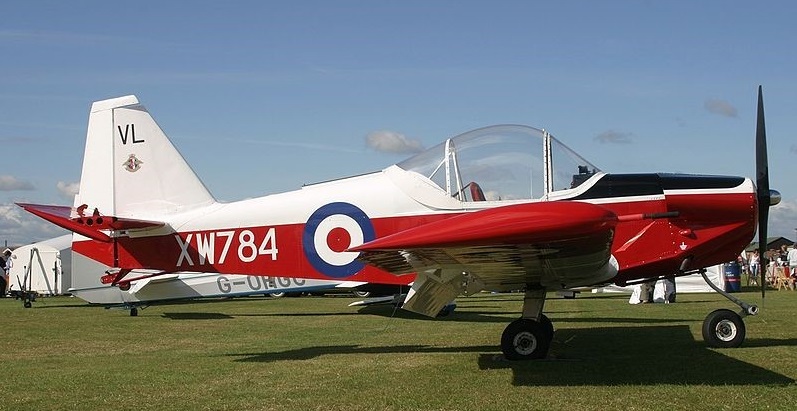

One Kittiwake was active until at least at 2005 and the other is still active. They remain on the UK Civil Register. These are the prototype, G-ATXN and the ex-Naval G-BBRN. The latter is painted, as in its Naval days, as XW784.
Kittiwake I
Engine: 1 × Rolls Royce-Continental O-200-A, 100 hp (75 kW)
Propeller: 2-bladed McCauley 69CM52, 5 ft 9 in (1.75 m) diameter metal, fixed pitch
Wing span: 24 ft 0 in (7.32 m)
Wing area: 105 sq ft (9.8 m2)
Length: 19 ft 7 in (5.97 m)
Height: 7 ft 6 in (2.29 m)
Empty weight: 910 lb (413 kg)
Gross weight: 1,250 lb (567 kg) for aerobatic flight
Maximum take-off weight: 1,350 lb (612 kg)
Fuel capacity 26 USG
Maximum speed: 131 mph (211 km/h; 114 kn)
Cruise speed: 122 mph (106 kn; 196 km/h) at 75% power
Stall 48 mph
Range: 540 miles (469 nmi; 869 km) at 92 mph (148 km/h)
Ferry Range with additional tanks: 600 miles (521 nm; 966 km)
Rate of climb: 850 ft/min (4.3 m/s)
Crew: 1