In 1958 a group of students from the faculty of aeronautical construction of the Moscow Aviation Institute (MAI) came together to create a construction bureau to build aircraft in a flying wing configuration. In this group the students A. Krivomlin, M. Alexandrov, Yu stood out. Belov, A. Bielosviet, V. Irinarjov, S. Kurilienko, Ye. Mizinov and V. Novikov among others.
The research carried out and the technical solutions of the LK-MAI would be used as the basis for the development of a new flying wing glider, which was called MAI-63 (Russian: МАИ-63).
The work began in the autumn of 1962 with the participation of members of the MAI sports aviation club under the direction of the head of the scientific-research sector AI Pitsuj. All the construction work was done by the students themselves.
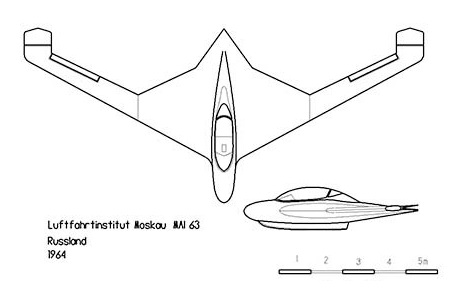
The glider design featured a low elongation centroplane with a rhomboid shape in the plane to which consoles were attached with 30º inflection on their leading edge. The sagging of the centerplane and the consoles was the same. Aerodynamic blades were located where the fuselage was attached to the consoles.
The large swelling of the wings made it possible to locate double-surface elevator rudders (“crocodile” type) on the trailing edge of its extremities. This location guaranteed an adequate balance of the apparatus even with the flaps extended. The ailerons, located on the trailing edge, were of the conventional type.
The glider lacked a horizontal empennage. Longitudinal control was performed by a combination of the elevator rudders. When the left pedal was depressed, the surfaces on the left side opened up, increasing the resistance at that end, and the aircraft turned to the left. By keeping the pedals in a neutral position, both surfaces joined to form a single rudder.
The cockpit was designed to accommodate a semi-reclining pilot and was covered with a bubble-type lantern.
The entire construction was made of metal. The wing design had a laminar profile. The covering of the centroplane and the wing up to the middle of the chord was made of duralumin and from there on in fabric.
The landing gear was unicycle type with the wheel located on the axis of the device and conveniently fairing. In the rear area there was a amortized skate. Stabilization supports with small wheels were placed under the wing tips.
In 1963 the project for the new glider was ready and in that same year construction began in the workshops of the laboratories of the MAI aircraft construction and projection chair. The prototype was ready for 1964.
In the construction of the model stood out V. Rytsariev, G. Bespalov, O. Tischenko, Ye. Volkov, A. Turik, S. Turchkov, V. Fatyanov, V. Vasiliev, and V. Pushkin.
All the turning and milling jobs were developed by students. Many of them had the necessary qualifications and were masters of the sport in model aircraft. This made the job easier.
The 5th year student Yu. Shirokov, who designed the centroplane and the cockpit, was still in his school years champion of Moscow in model aircraft; V. Pushkin had attended various professions.
Structural strength calculations were developed by M. Stolyar, O. Derzhavin, V. Voronin, and V. Kuznietsov. As a consultant, Ye acted. S. Voit.
The MAI-63 tests were developed in Alferiev in 1964 and were in charge of AI Pietsuj. Several towed flights
were made approaching take-off speed, piloted by AI Pietsukh. Structural strength problems led to the decision no flights were done.
After the first tests, several corrections were made to the apparatus: the wing structure was reinforced and modifications were made to the landing gear.
In 1965, MAI-63 was modified to a motor-glider installing on a pole erected over the central part of the glider an air-cooled EP-760 23 HP, five-cylinder, two-stroke radial engine. The engine was designed by Polyakov specifically for motor-gliders and light aircraft. The modified glider got the designation MAI-63M. Tests were conducted at the flying club’s airport. The engine during the trial taxi runs was unstable so the powered version of the glider was never flown.
MAI-63
Wingspan: 12.60 m
Wing area: 9.00 m²
Aspect ratio: 17.5
Wing profile: Laminar
Empty weight: 126 kg
Normal weight: 200 kg
Wing loading: 22.2 kg / m²
Best glide ratio: 35
Descent speed: 0.61 m / s
Accommodation: 1