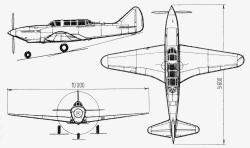
Developed in the late 1930s by the Moscow Aviation Institute in the OKB-1 led by PD Grushin, was a ground attack aircraft and light bomber that received the designation MAI/Grushin BB-MAI (Russian: МАИ/Грушин ББ-МАИ).
The BB-MAI was designed as a classic monoplane layout airplane with a 1050 hp M-105 powerplant and was designed during 1938 and 1939.
The BB-MAI introduced the use of bakelite plywood construction, introduced with the help of a group of specialists from VIAM, the engine used a compressor that worked with exhaust gases, developed by TsIAM, for the first time in the USSR, a nose Wheel undercarriage, and a movable turret.
The double-spar wing was made up of three C-sections made of Bakelite plywood. When these sections were joined together, the “back” formed the spar wall and its base became the wing covering. The sections were glued with VIAM B-3 glue during assembly, producing a structure of considerable rigidity. The wing area was small at 15.2 m², therefore, with a takeoff weight close to 3,500 kg, the wing loading reached 210 kg/m². The wing also had automatic slats.
The coating on the base of the wing reached 5 mm and on the tail section 3 mm. The walls of the stringers were 25 mm. The fuselage was of the monocoque type made of bakelite plywood glued with the same glue. This construction achieved such strength that the internal structure could be lightened. As in the case of the Grushin Sh-Tandem, the surface was highly polished.
The main wheels were retracted towards the wing, to the sides of the fuselage, with a 90º turn of the wheels. Behind the front wheel was the radiator.
Construction of the prototype began in 1939 and it was completed in 1940 at KBMAI. The main builder of the prototype was AA Lebiedinski and AA Manucharov was appointed as the main test engineer. The BB-MAI was tested by MAI graduate AN Grinchik, a Soviet test pilot who would die in a crash in the USSR’s first turbojet aircraft.
Construction delays led to the first flight taking place in December 1941. By that time the interest of the VVS for an aircraft with these characteristics had already disappeared. Grushin himself had been appointed KB ‘s main builder at Kharkiv Aviation Factory (JAZ) No.135 and KB MAI was soon shut down for a few years.
Only one prototype was built and flown in the December 1941. The proximity of the war led to the end of the project. The BB-MAI was never armed.
Powerplant: 1 x 1050 hp М-105
Wing span: 10.00 m
Wing area: 16.80 m²
Length: 9.60m
Empty weight: 2965 kg
Normal takeoff weight: 3490 kg
Wing loading: 208 kg/m²
Power load: 3.3 kg/hp
Maximum speed at sea level: 508 km/h
Maximum speed at altitude: 550 km/h
Ascent time to 5000 m: 9.2 min.
Practical range: 500 km
Practical ceiling: 9000 m
Accommodation: 2