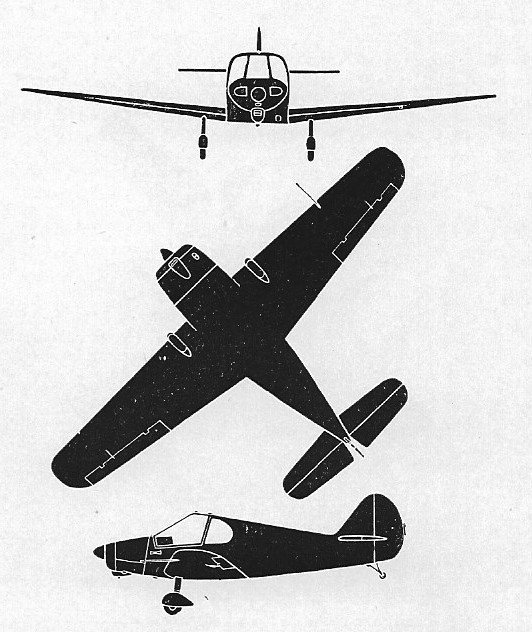
M. Yves Gardan designed the GY 201 Minicab in 1949 as a two seater with side by side seating and dual control, which first flew in 1949. The fuselage is a wooden open girder structure; the forward part around the cockpit being plywood lined, the remainder fabric covered. The fin is built integral with the fuselage. The tailplane is a single piece plywood covered structure, and the elevator and rudder have fabric covered wooden frames. The wing section is NACA 23015 at the root and 23010 at the tip. The wing structure consists of a laminated spruce and plywood main box spar, a diagonal drag spar and a rear false spar, with lattice type ribs. Forward of the main spar is plywood covered to form a torsion box, the remainder of the wing being fabric covered. Split flaps are installed. The two main undercarriage legs are mounted on the main spar with rubber in compression springing. An 11 Imp. gallon fuel tank is fitted just behind the firewall.
The GY-20 Minicab first flew in February 1949.
In 1949 his GY 20 Minicab won the world record for speed and distance in a straight line for an aircraft of less than 1102 lb (500kg) maximum gross weight, flying from Paris to Rabat in 10h of flight, 1135 mile being covered at 109mph average (1826km at 185kph) with a Continental 65hp motor. More than 100 Minicabs were made and it is still being built by US homebuilders under the name of Cavalier in 1983.
In 1952, the 90hp version of the Minicab appeared, with retractable undercarriage and called the Super Cab.
Continental engines from 65 to 100 h.p. may be installed.

Production was entrusted to the Constructions Aernautiques du Bearn, which delivered the first aircraft in 1952, and support for this light type subsequently passed to SIPA (the Société Industrielle Pour l’Aeronautique). There were two production variants of the Minicab, the GY.20 and GY.201, these differing from each other only in details of equipment and other small features.

The GY-30 Supercab first flew in February 1954 with refinements including retractable undercarriage, fixed tip tanks and 90 hp Continental C-90. Two of a pre-production batch of five were ordered for evaluation by the Service de l’Aviation Legeres et Sportive.

One of the French G.A.B. Supercabs was undergoing fully-instrumented test flying at Villacoublay; Jacques Noetinger is the pilot.
Produced in limited numbers between 1952 and 1958, the design was acquired by A.W. Ord-Hume in Britain, who anglicised the plans. Adjusted them for home builders, the aircraft has subesequently proved extremely popular. The aircraft is marketed in North America as the Hawk BM.4 by Miranda Aircraft of Canada.
Variation:
Barritault JB.01
GY-20
Engine: Continental A65-8, 65 hp
Wingspan: 24 ft 11 in
Length: 17 ft 10.5 in
Height: 5 ft 5 in
Wing area: 107.6 sq.ft
Empty weight: 595 lb
Loaded weight: 1069 lb
Max speed: 124 mph
Cruise: 112 mph
ROC: 680 fpm
Range: 466 mi
Engine: l x Continental A65-8, 48.5kW (65hp).
Span: 7.59m (24ft 11 in).
Length: 5.45m (17 ft 10.5 in).
Max T/O weight: 485 kg (1,069 lb).
Max speed: 124 mph at sea level.
Operational range: 466 miles.
Seats: 2
Engine: Continental, 90 h.p.
Span: 25 ft 0 in.
Length: 17 ft 0 in.
Wing Area: 107 sq. ft.
Empty Weight: 750 lb.
Loaded Weight: 1235 lb.
Wing Loading: 11.5 lb/sq. ft.
Max. Speed: 124 mph.
Cruise Speed: 110 mph.
Stall Speed: 50mph.
Initial Climb: 680 fpm.
Range: 360 miles.
Engine: Continental O-200A, 100 h.p.
Cruise: 120 mph
ROC: 1000 fpm.
Span: 25ft
Length: l7ft l0in
Empty weight: 800lb
Gross weight: 1234 lb
Engine: Revmaster VW, 65 hp. Stall: 38 kt / 43 mph / 70 kmh
Cruise: 97 kt / 112 mph / 180 kmh
VNE: 107 kt / 123 mph / 198 kmh
Empty Weight: 270 kg / 595 lbs
MTOW Weight: 485 kg / 1069 lbs
Climb Ratio: 600 ft/min / 3 m/s
Take-off distance (50ft obstacle): 1150 ft / 350 m
Landing distance (50ft obstacle): 1080 ft / 330 m
GY-30 Supercab
Engine: Continental C90, 90 hp
Max speed: 170 mph
Cruise: 146 mph
ROC: 767 fpm
Service ceiling: 16,400 ft
Range: 746 mi
Empty weight: 880 lb
Loaded weight: 1348 lb
Wingspan: 26 ft 10 in
Length: 18 ft
Height: 5 ft 5 in