The Technological Research Institute constituted the technical base on which Companhia Aeronáutica Paulista emerged. The Institute designed two aircraft that came to be manufactured in series by this company, in addition to designing the Paulistinha aircraft, it was the Paulistinha project, passed on to Companhia Aeronáutica Paulista (CPA) together with the Planalto plane that generated the first royalties paid to the IPT.
Neiva P-56 Paulistinha Article
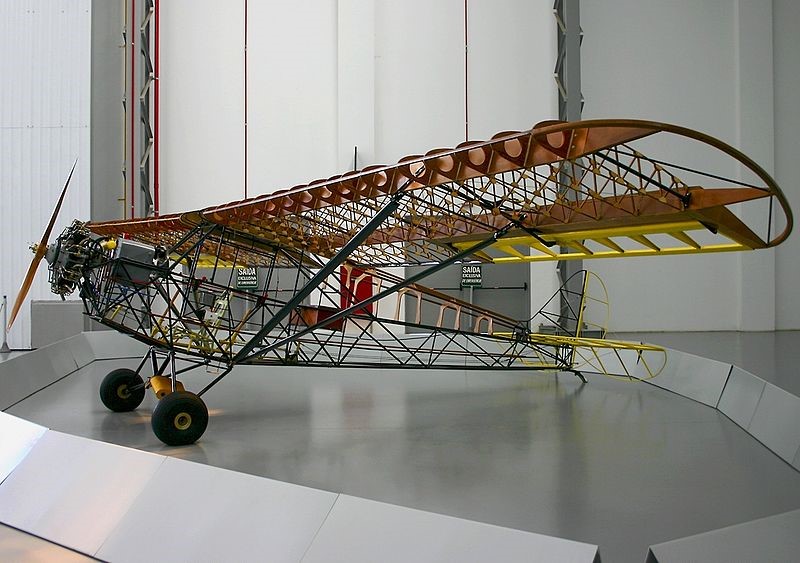

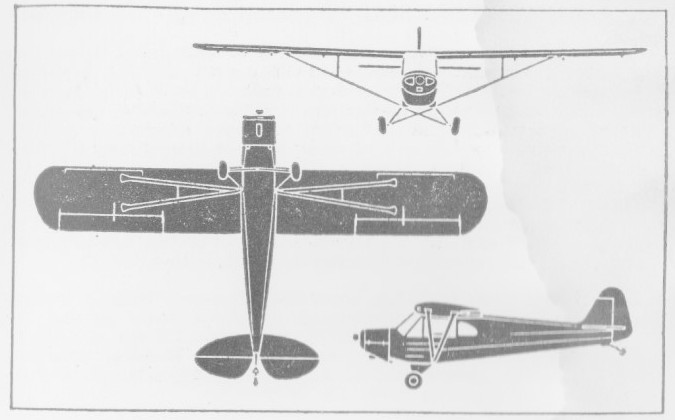
Originally developed by Empresa Aeronáutica Ypiranga (EAY) as an unlicensed copy of the Taylor Cub powered by a Salmson 9Ad radial engine, the EAY-201 featured a high strut-braced wing, two enclosed tandem seats, and a steel-tube fuselage with fabric covering. Its tailwheel undercarriage was not retractable.

First flown in 1935, EAY had built five examples by the time that the firm was purchased by Companhia Aeronáutica Paulista (CAP) in 1942. CAP continued manufacturing the type under the designation CAP-4 with a 65 hp Franklin engine.
The Paulistinha was produced in three versions. The CAP 4 Tourer, the CAP 4B ambulance aircraft, and the CAP 4C military observation monoplane. The CAP 4C had a cut-down rear fuselage with the side windows extended aft.
Production of the Paulistinha was stopped in 1948, when the Paulistta company experienced financial difficulties, and resumed in 1956 by the Sociedade Construtora Aeronautica Neiva as the Pulistinha 56 (90 hp Continental C90-8F) and 56-B (100 hp Lycoming). The Paulistinha 56-C appeared in 1958, and 210 had been delivered by mid-1963. The Paulistinaha L-6 (100 hp Lycoming) was a liason version for the Brazilian Air Force, 19 being delivered in 1959.
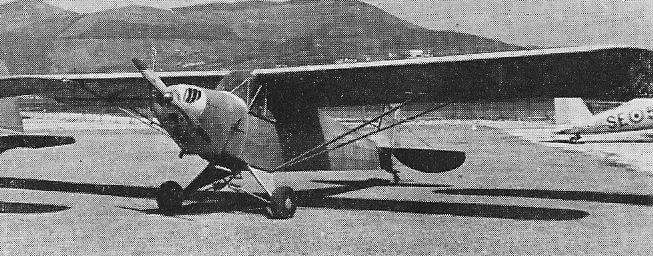
The type was widely successful, with nearly 800 units being produced for Brazil’s flying clubs and armed forces, as well as for export to Argentina, Paraguay, Chile, Uruguay and Portugal. At the time of peak production in 1943, a new CAP-4 left the factory every day, and production continued until 1948 when the company enter financial difficulties.

In 1956, Sociedade Aeronáutica Neiva (Neiva) acquired the rights renaming it to P-56 Paulistinha, the design was used as the basis for an agricultural aircraft, the P-56 Agricola, adding a fibreglass chemical hopper and spraybars, but this was unable to compete with imported, purpose-built agricultural aircraft.
In dimensions and characteristics, it is similar to the last series of the Paulistinha CAP-4 produced by Companhia Aeronáutica Paulista , from which Neiva acquired the rights, launching a new version, named Paulistinha 56 or Neiva 56.
First flying in 1955, the Neiva P-56 Paulistinha could be equipped with a Continental C-90-8F or C90-12F engine, which could develop up to 115hp at 2625 RPM. A total of 256 were built
Its fuel system consists of two gas tanks, one at the top of the cabin and the other between the instrument panel and the engine fire wall, before entering the carburetor the gasoline passes through a filter and decanter type “cup” “.

The Brazilian Air Force operated this aircraft between 1959 and 1967, with the military designation L-6 . It was used in bombing connection, observation and calibration missions. Paraguayan Military Aviation bought four aircraft in the early 1960s. The Paraguayan Aeroclub bought four aircraft in the 1950s
In total about 840 were built.
Variants:
EAY-201
original version
Engine: Salmson 9Ad
Seats: 2
CAP-4 Paulistinha
main production version
Engine: 1 × Franklin 4AC, 48 kW (65 hp)
Wingspan: 10.10 m (33 ft 2 in)
Wing area: 17.0 m2 (183 sq ft)
Length: 6.65 m (21 ft 10 in)
Height: 1.95 m (6 ft 5 in)
Empty weight: 320 kg (705 lb)
Gross weight: 540 kg (1,190 lb)
Fuel capacity: 58 L (15 US gal; 13 imp gal)
Maximum speed: 155 km/h (96 mph, 84 kn)
Cruise speed: 140 km/h (87 mph, 76 kn)
Range: 500 km (310 mi, 270 nmi)
Service ceiling: 4,000 m (13,000 ft)
Rate of climb: 3.1 m/s (610 ft/min)
Crew: Two, pilot and instructor
CAP-4B
air ambulance version (2 prototypes built)
Engine: 1 × Franklin 4AC, 48 kW (65 hp)
Wingspan: 33 ft 2 in
Length: 21 ft 10 in
Height: 6 ft 4.75 in
Empty weight: 706 lb
Loaded weight: 1190 lb
Max speed: 96.5 mph
Cruise: 87 mph
ROC: 610 fpm
Range: 311 mi
CAP-4C
artillery-spotting version, (Paulistinha Rádio or Paulistinha Observação)
Engine: 1 × Franklin 4AC, 48 kW (65 hp)
Wingspan: 33 ft 2 in
Length: 21 ft 10 in
Height: 6 ft 4.75 in
Empty weight: 706 lb
Loaded weight: 1190 lb
Max speed: 96.5 mph
Cruise: 87 mph
ROC: 610 fpm
Range: 311 mi
P-56 Agricola
agricultural version by Neiva
60 built
Neiva P-56 Paulistinhab
Engine: Continental C90-8F, 90 hp
Wingspan: 10.8 m (35 ft 4 in)
Wning area: 183 sq.ft
Length: 6.90 m (22 ft 2 in)
Height: 1.95 m (6 ft 5 in)
Empty weight: 882 lb
MTOW: 1455 lb
Max speed: 100 mph at SL
Cruise: 90 mph
ROC: 875 fpm
Ceiling: 19,685 ft
Range: 560 mi
Endurance: 4 hrs
Neiva Paulistinha 56-C
Engine: Continental C-90-8F/12F, 90 hp (67 kW)
Seats: 2
256 built by between 1958 and 1964.
P56C-1 Paulistinha Rebocador
Paulistinha 56-D
Engine: Lycoming O-320-A1A, 150 hp (110 kW)
Single prototype built
Brazilian Air Force designated L-6A
No production.