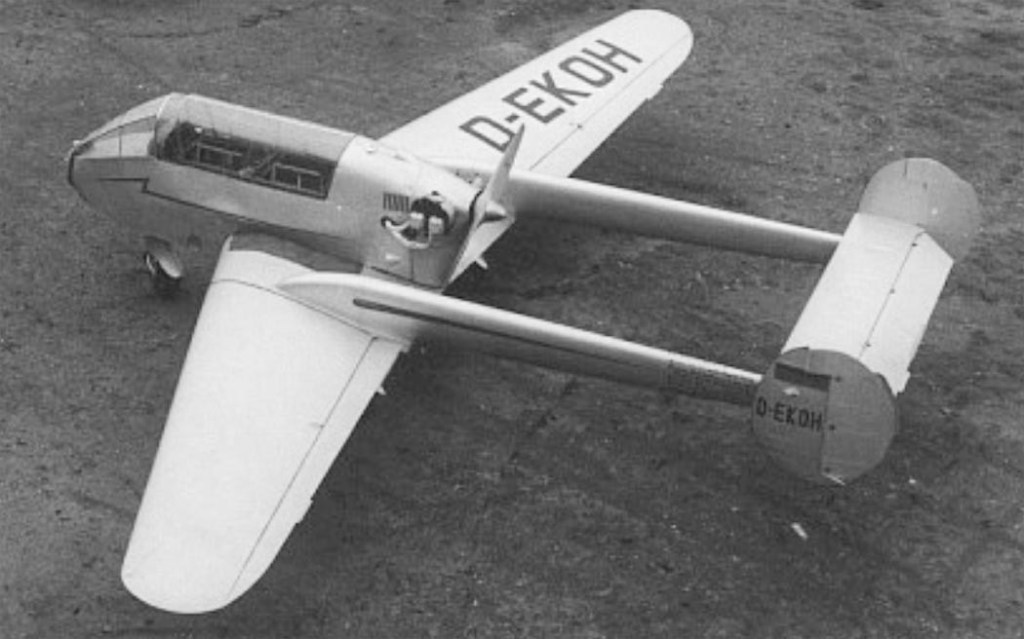
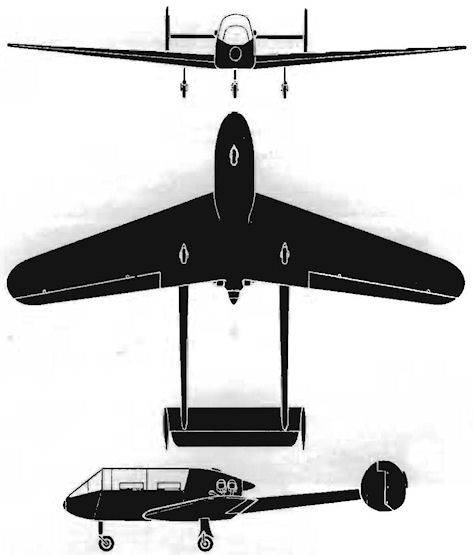
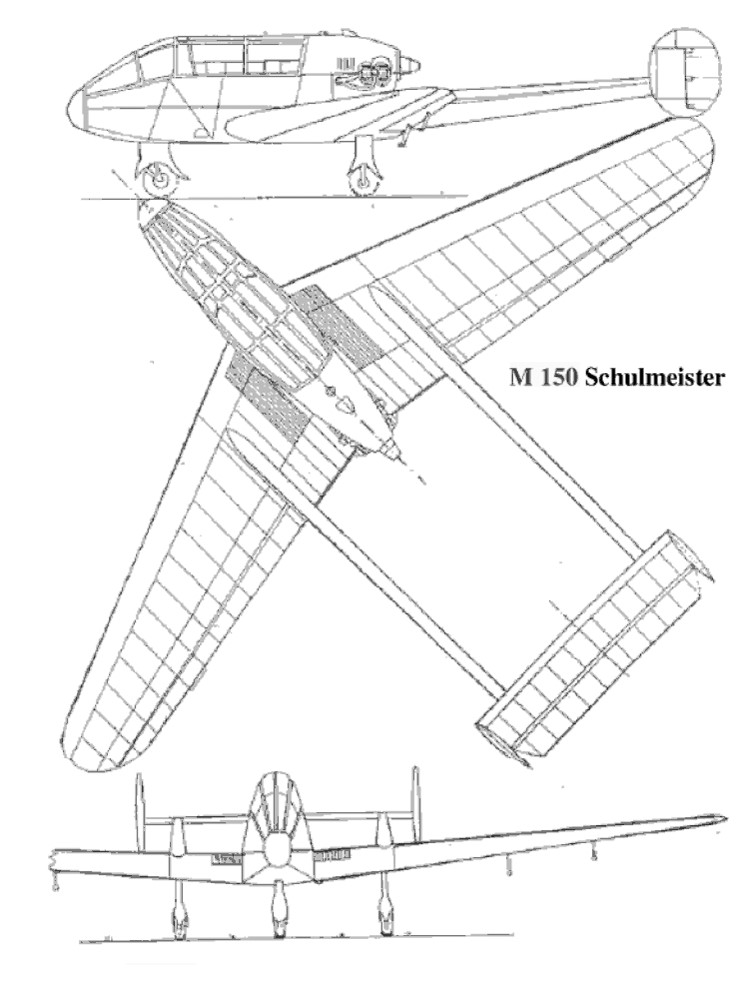
Developed from the A-15 (WN-16) aircraft, designed by the former Wiener-Neustadt company, the M-150 Schulmeister (Schoolmaster) is a two-seat, low-wing type, powered by a 65 hp Continental C90 incorporating a pusher propeller.
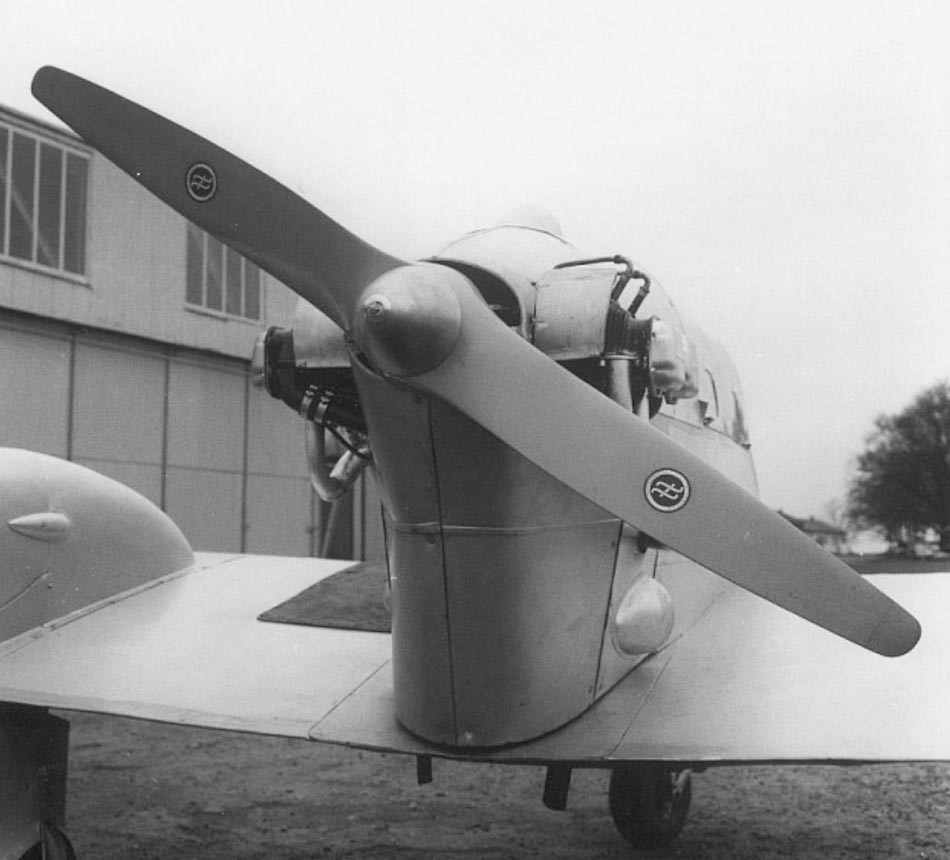

In the early 1950s, the German company Burgfalke Segelflugzeugbau became interested in the aircraft. Maidl modernized the project to meet new requirements resulting in 1956, with the M-150 Schulmeister.

The M-150 is capable of simple aerobatics, and the makers claim that it is almost impossible to spin even under extreme flight conditions. Construction is of mixed wood and steel, the main structural members being of steel. The wing and tail units are mostly of wood, with the leading edge and undersides ply covered, and the upper surfaces fabric covered. Fuselage is of a tubular structure and fabric covered.
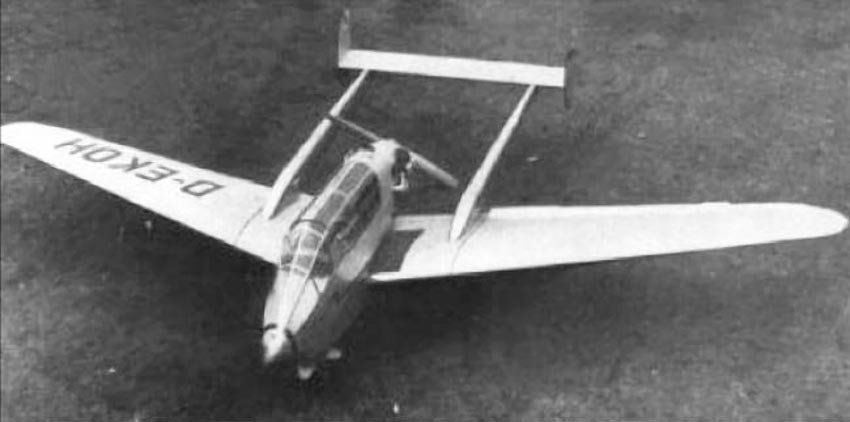

The prototype aircraft first flew on September 14, 1957. Having received the civil registration D-EKOH in the same year, the aircraft was tested, but could not interest potential customers.

M-150
Engine: Continental C90, 90 hp
Wingspan: 9.84 m
Wing area: 13.50 sq.m
Length: 7.27 m
Height: 1.80 m
Empty weight: 350 kg
Maximum takeoff weight: 590 kg
Maximum speed: 165 km/h
Cruise speed: 145 km/h
Practical range: 500 km
Practical ceiling: 4200 m
Crew: 2