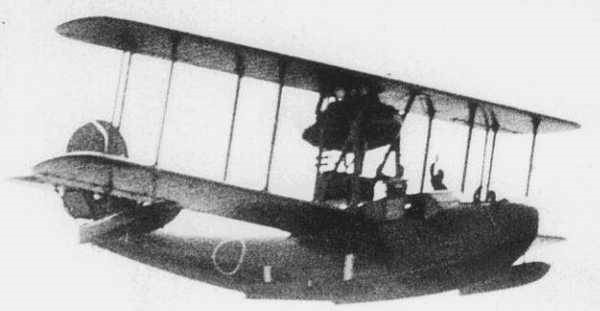
In 1934, based on experience of testing the Experimental 6-Shi Night Reconnaissance Flying boat, the Imperial Japanese Navy drew up a specification for a new night reconnaissance aircraft, intended to shadow enemy fleets during the cover of darkness, with orders being placed with Aichi and with Kawanishi.
Aichi’s design, with the company designation AB-12, was a single-engined biplane flying boat of all-metal construction. Its two-bay wings folded rearwards to save space on board ship, while its crew of three were accommodated in an enclosed cabin. It was powered by a pusher water-cooled Aichi Type 91 engine, driving a four-blade wooden propeller.
The first prototype flew in December 1934, and when tested proved to have superior stability to the competing Kawanishi E10K, and so was ordered into production.
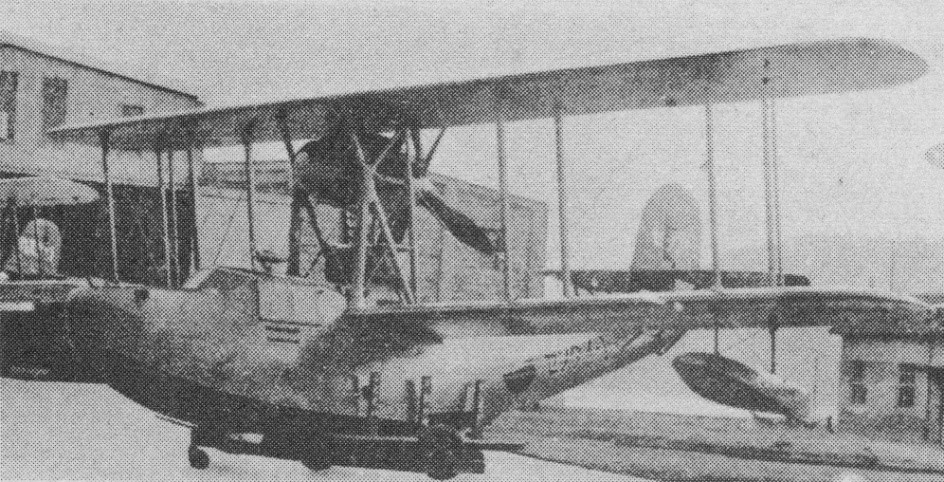
The AB-12 entered service in August 1936 with the Japanese Navy as the Type 96 Night Reconnaissance Seaplane, with the short designation E10A. The allied code name ‘Hank’ was assigned before its appearance or manufacturer was known.
Fifteen aircraft were built for the Imperial Japanese Navy serving from 1936, remaining in service until 1941, being phased out in 1941 before the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbour.
E10A
Powerplant: × Aichi Type 91 W-12, 370 kW (500 hp) to 485 kW (650 hp)
Propeller: 4-bladed wooden fixed-pitch pusher
Wingspan: 15.5 m (50 ft 10 in)
Wing area: 52.1 m2 (561 sq ft)
Length: 11.219 m (36 ft 10 in)
Height: 4.5 m (14 ft 9 in)
Empty weight: 2,100 kg (4,630 lb)
Gross weight: 3,300 kg (7,275 lb)
Wing loading: 63.2 kg/m2 (12.9 lb/sq ft)
Power/mass: 0.113 kW/kg (0.069 hp/lb)
Maximum speed: 206 km/h (128 mph, 111 kn) at sea level
Cruise speed: 106 km/h (66 mph, 57 kn) at 1,000 m (3,281 ft)
Range: 1,852 km (1,151 mi, 1,000 nmi)
Service ceiling: 4,120 m (13,520 ft)
Time 3,000 m (9,843 ft): 17 minutes 42 seconds
Guns: 1× 7.7 mm machine gun flexibly mounted in nose
Crew: 3