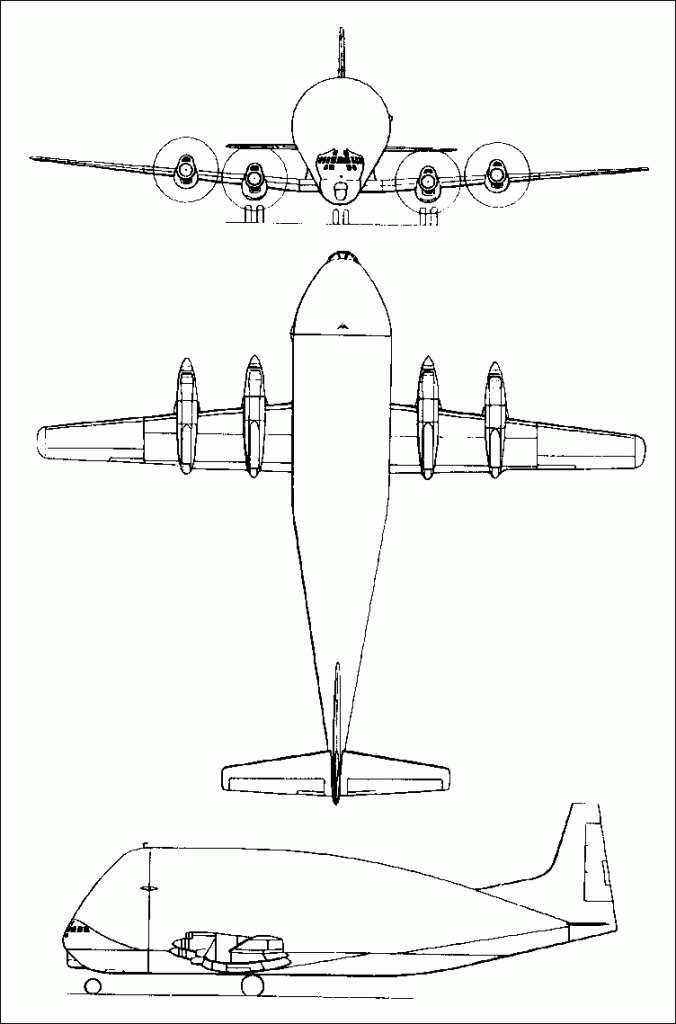
The Guppy 201 utilizes the lower fuselage, wings, tail unit and cockpit of a Boeing 377/C 97, with portions of the lower fuselage of several aircraft being joined to provide a larger cabin with interior diameter of 25′. Upper fuselage lobe added to stretched C-97 fuselage, plus parts from Airbus, Concorde, DC-10, and TriStar; engines from retired Lockheed Electras.
Although this Super Guppy is very close in dimensions to the original Super Guppy, the shape of the fuselage has a smoother flow and engine nacelles are completely different.

The first 377SGT Super Guppy Turbine flew on August 24, 1970. After success with the first of the 377SGTs, Aero Spacelines built a second 377SGT and it flew exactly two years later on August 24, 1972.
Aero Spacelines originally planned to build and operate the MGT and SGT aircraft but after the company got into serious financial trouble a decision was made to sell the SGT to Airbus Industrie.
Two were built by Aero Spacelines in early 1970s, N211AS and N212AS, and sold to Airbus Industrie/Aérospatiale to haul components of A300Bs and Concordes.
Two were built in early 1980s for Airbus by UTA Industries in France. Retired by Airbus in early ’90s; reportedly three went to European museums, and the last one was bought by NASA.

The Super Guppy Turbine (NASA’s B377SGT), super-sized cargo plane flown since 1980 was acquired by NASA in 1997. Its home base, was the Ellington Field, near the Johnson Space Center in Lancaster, California.

Guppy 201
Engines: 4 x Allison 501-D22C, 3663kW / 4912shp
Take-Off Weight: 77111 kg / 170002 lb
Empty Weight: 45359 kg / 100000 lb
Payload: 25000kg / 55116 lb
Wingspan: 47.63 m / 156 ft 3 in
Length: 43.84 m / 143 ft 10 in
Height: 14.78 m / 48 ft 6 in
Wing Area: 182.51 sq.m / 1964.52 sq.ft
Max. Speed: 460 km/h / 286 mph
Cruise Speed: 407 km/h / 253 mph
Ceiling: 7620 m / 25000 ft
Range W/Max.Payload: 813 km / 505 miles